An interesting set of results from my time with Boost. I cant wait to return to AIMI with what I have learned.
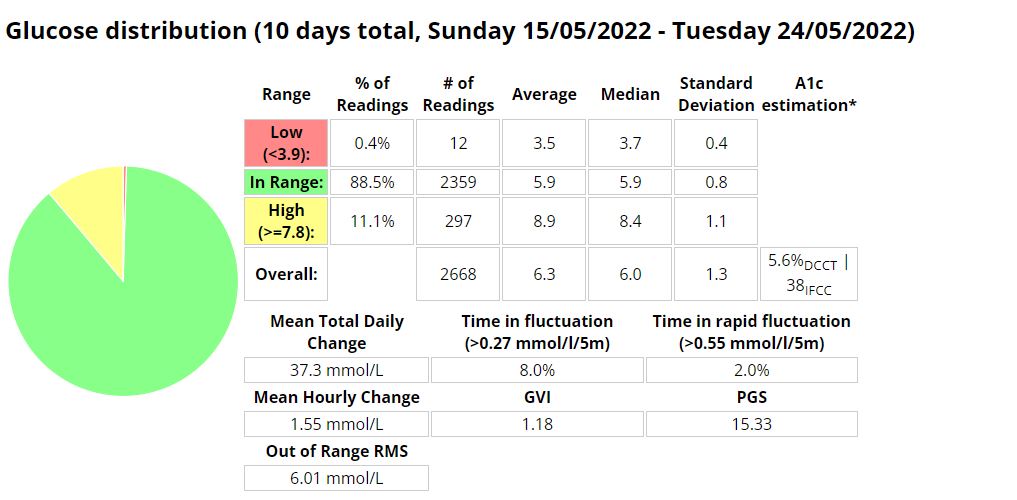
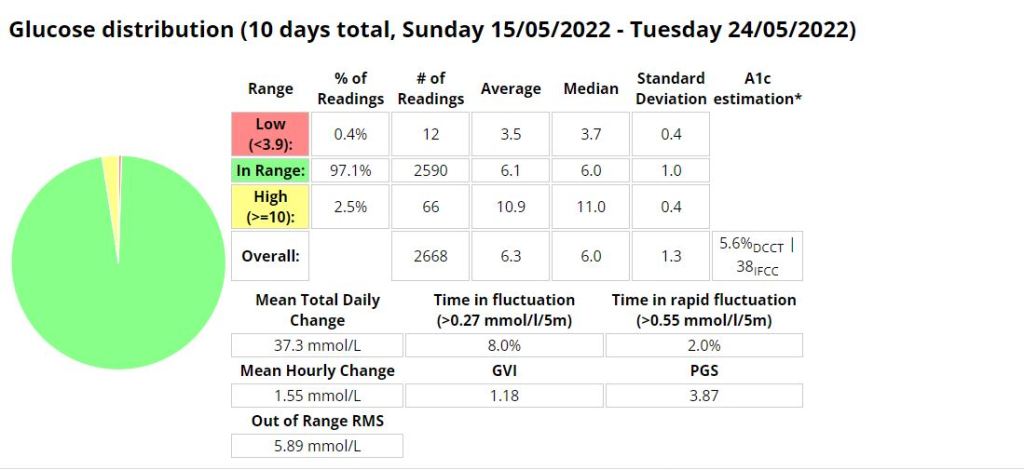
I was eating slightly less carbs (118g vs. 136g) than when I was using AIMI, but I would expect that if your profile is setup correctly that the amount of carbs shouldn’t have much of an impact on performance metrics. I was running into a few hypos so I lowered the algorithms insulin required percentage (70% vs. 100%) which resulted in a whopping 1.6% decrease (57 minutes vs. (288 minutes / 4.8 hours)) of time spent in a hypoglycaemic state while using Boost.
My standard deviation was slightly lower (1.3 vs. 1.4) signifying less fluctuations between readings while my time in a hyperglycaemic state went up 0.6% (25.2 hours vs. 26.6 hours)).
I did have to turn off “enable boost percentage scale” as this was providing too much insulin, but more experimenting could remedy this.
Another interesting observation was that my ratio between total daily dose (TDD) and total carbs eaten went down from 4.2 to 4.01 (grams of carbs per unit of insulin) as my average blood sugar lowered.
My exercise seems to have stayed pretty consistent during testing (as per the table below) which leads me to believe the reduced insulin need may be related to requiring less insulin when blood sugar is euglycemic. Its going to be a little more difficult to track that for the next few weeks as I am preparing to ramp up training for the Southern Cross 10km in July. The training has however provided an opportunity to fine tune my running routine as outlined here in my post about predicting blood sugars while running.
I cant wait to do some further testing with AIMI, Boost and Eating now.