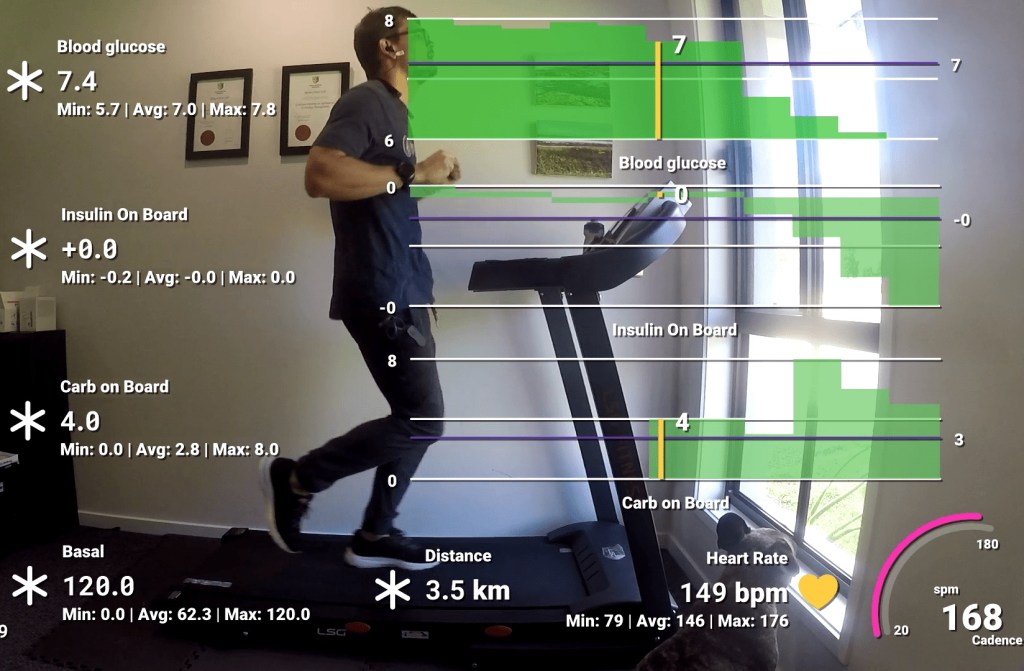
It’s spring, and after a brief ‘almost two months’ of going off the reservation snacking at all times of day and barely exercising, I decided to check my weight. I discovered I had picked up a few kilograms since my last weigh in. After learning this, I decided that it was time for me to get my life back together and start another 30 day challenge. I find these great to provide the reason to get back into a routine.
I know that setting unrealistic goals (like losing 5kgs) isn’t going to work, so I’m going to break down my plan in to nutrition, exercise and diabetes goals.
Exercise
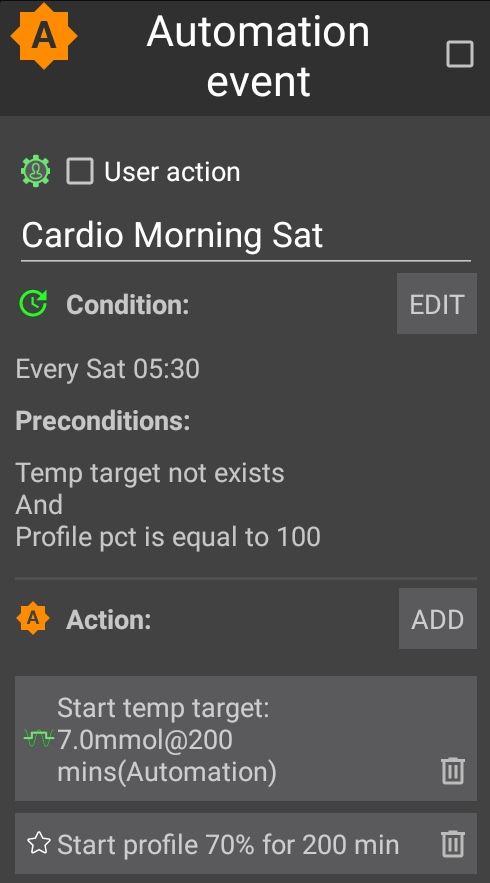
My plan for the month is to gym three days a week, run a minimum of 2 times per week and to mountain bike at least once a week. (So I guess I lied about setting unrealistic goals 🙂 )
Nutrition
For my meals I plan to stick to my usual low-ish carbohydrate meals during the week and try to only go coo-coo bananas on the late night snacking over the weekend. I’ll start carb-counting again as this will almost always yield the best results. This will be supplemented with 2-3 liters of water, depending on length of cardio that day.
Diabetes
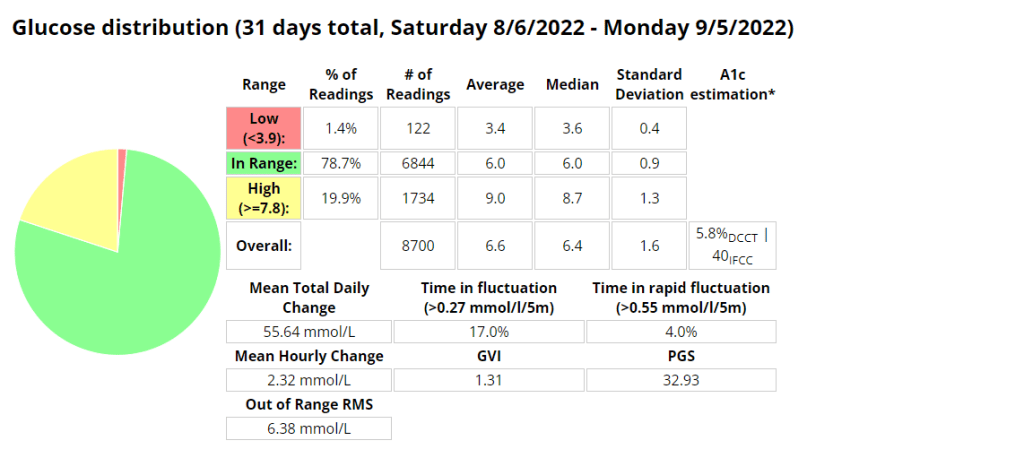
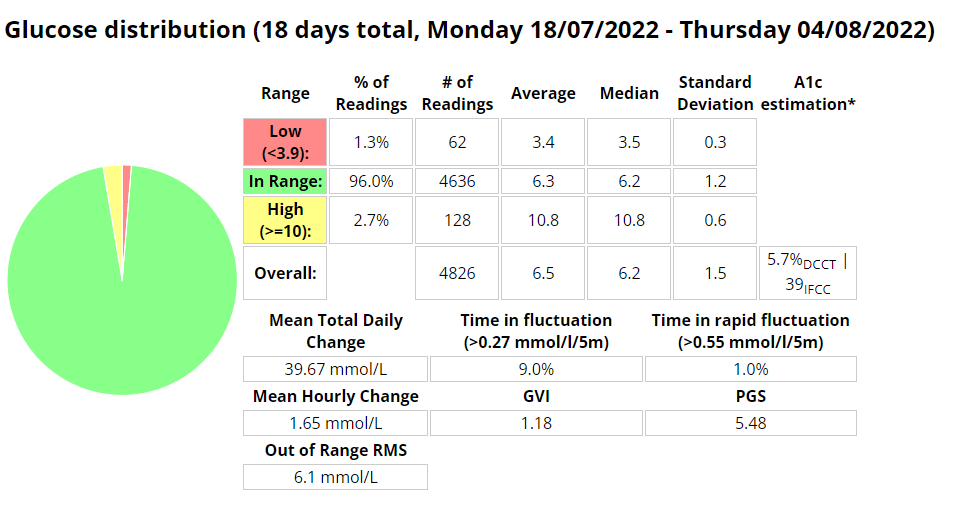
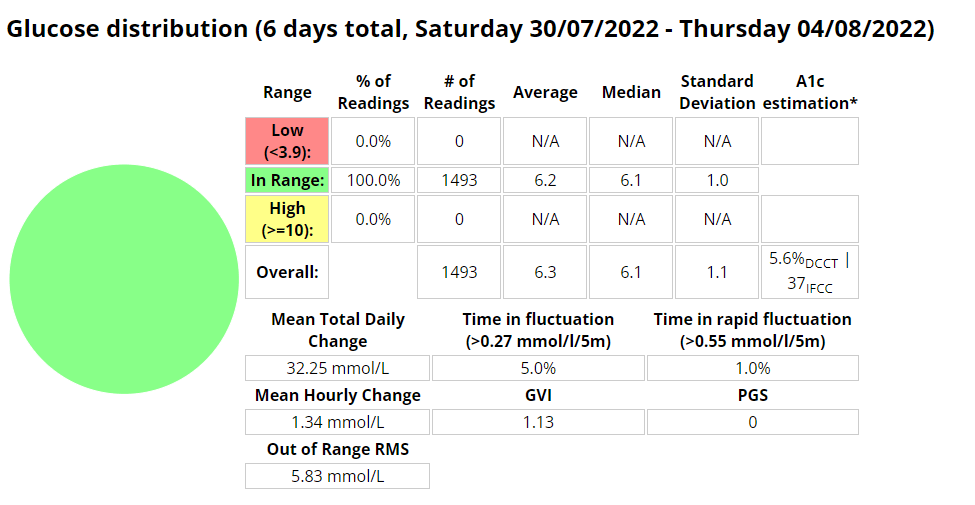
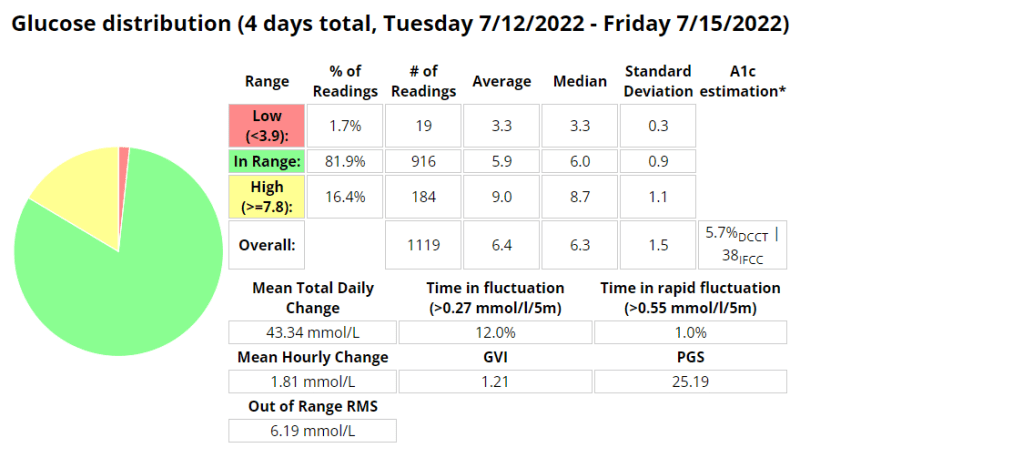
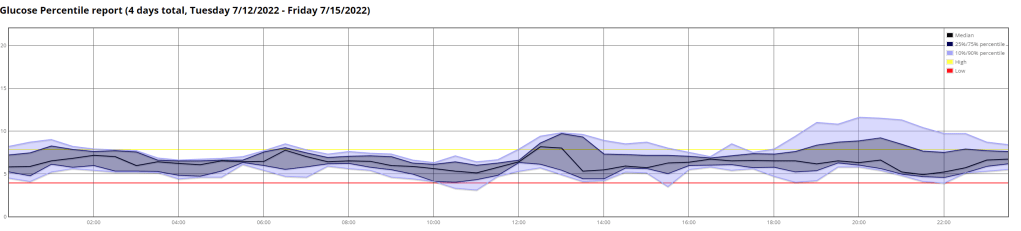
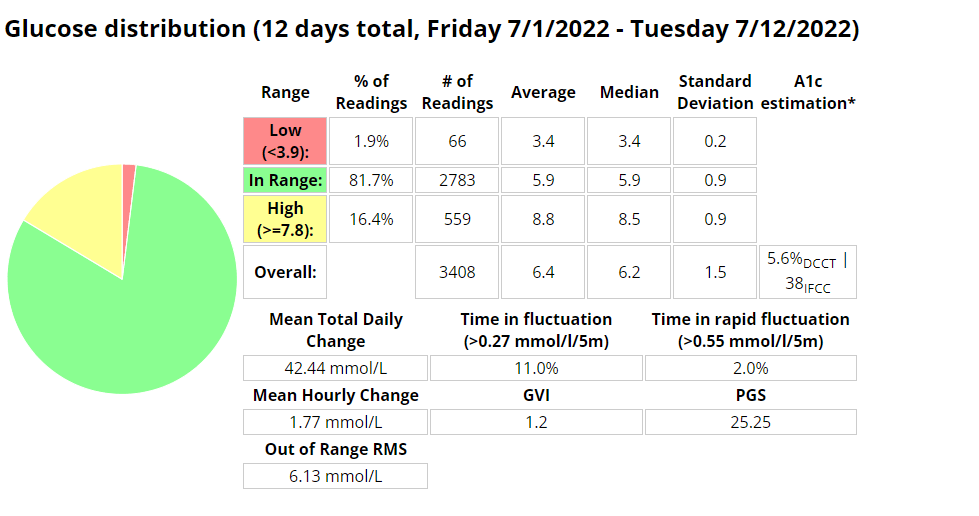
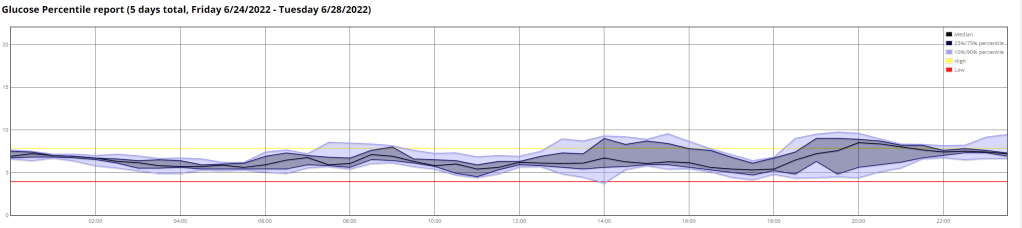
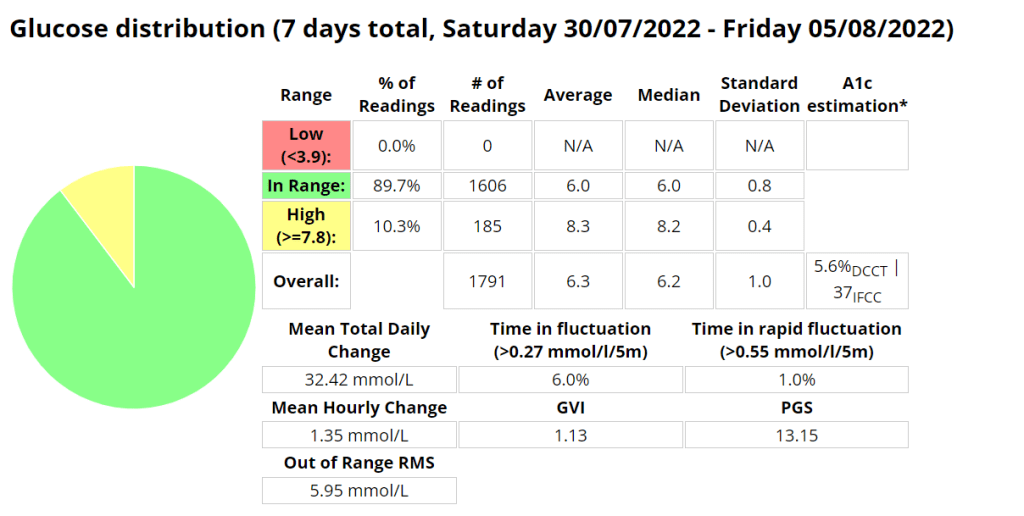
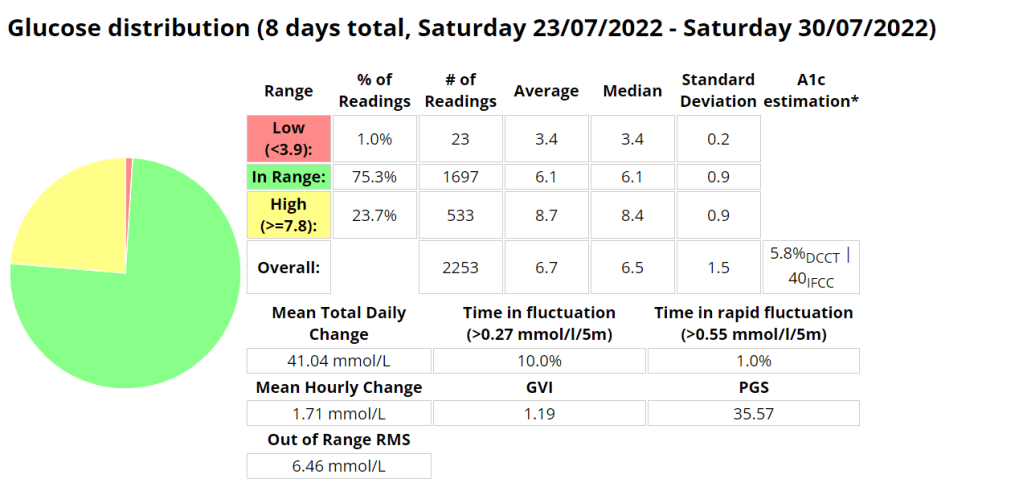
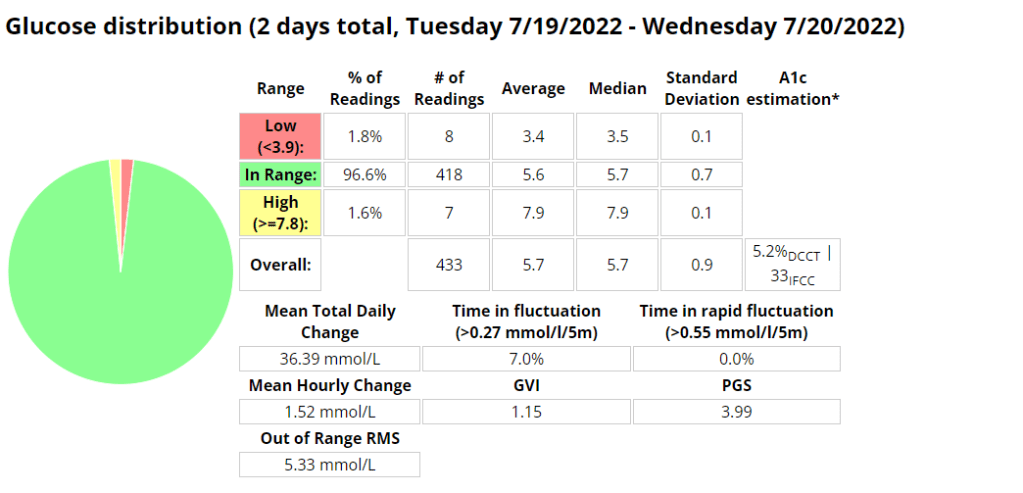
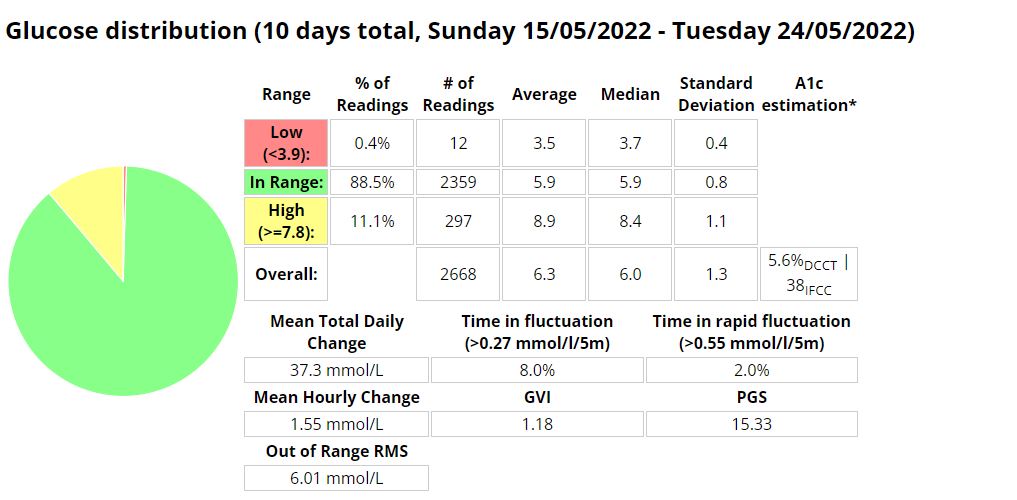
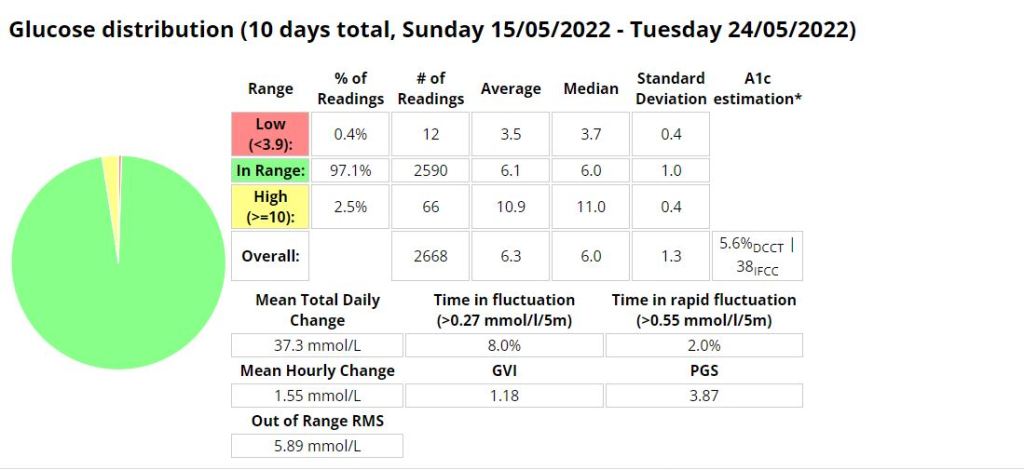
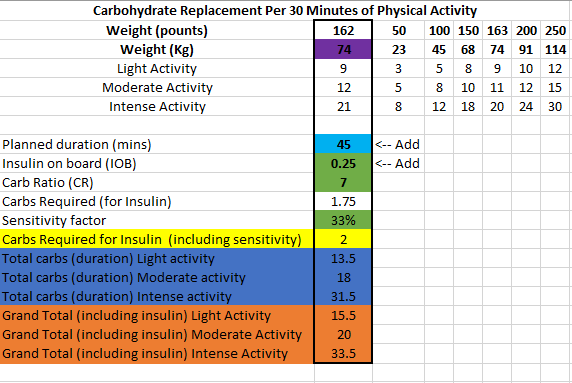
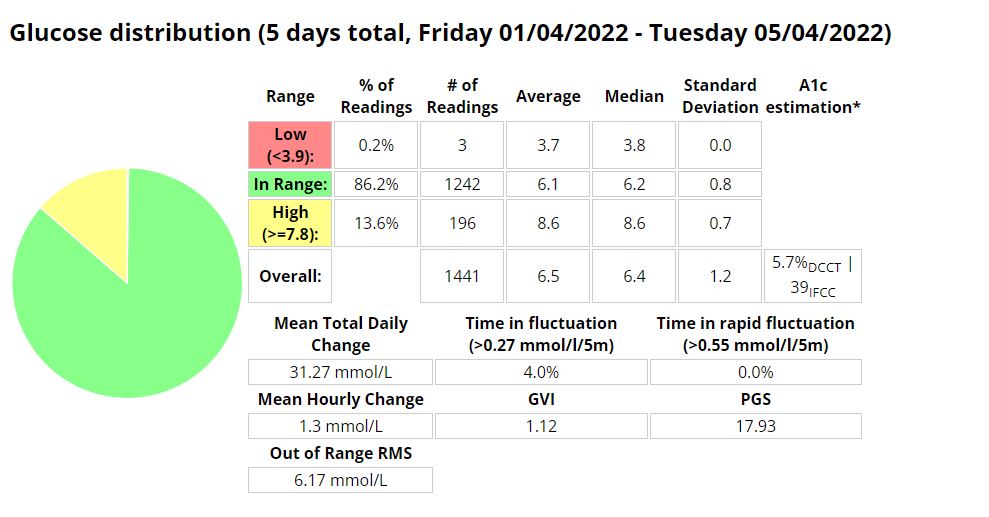
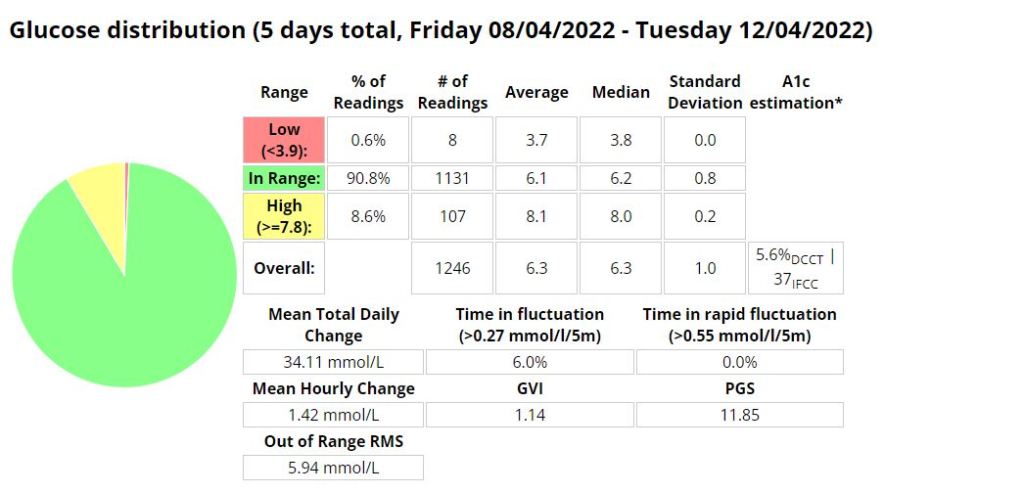
Above is a chart of my starting metrics. Lets see how quickly I can improve those values. Its going to be a little bit of an unfair test as I was not carb-counting during the above period.
We want to see the In range (Time-in-range) increase and the standard deviation decrease. By doing that the average and the A1c should follow. This will mostly be achieved by the diet component of the plan. The exercise component will allow me to eat more cabs and require less insulin, as well as improve circulation, sleep, blood pressure, mood, cholesterol, memory and overall mental and physical health.
I will check in with weekly updates to ensure I keep motivated and accountable.