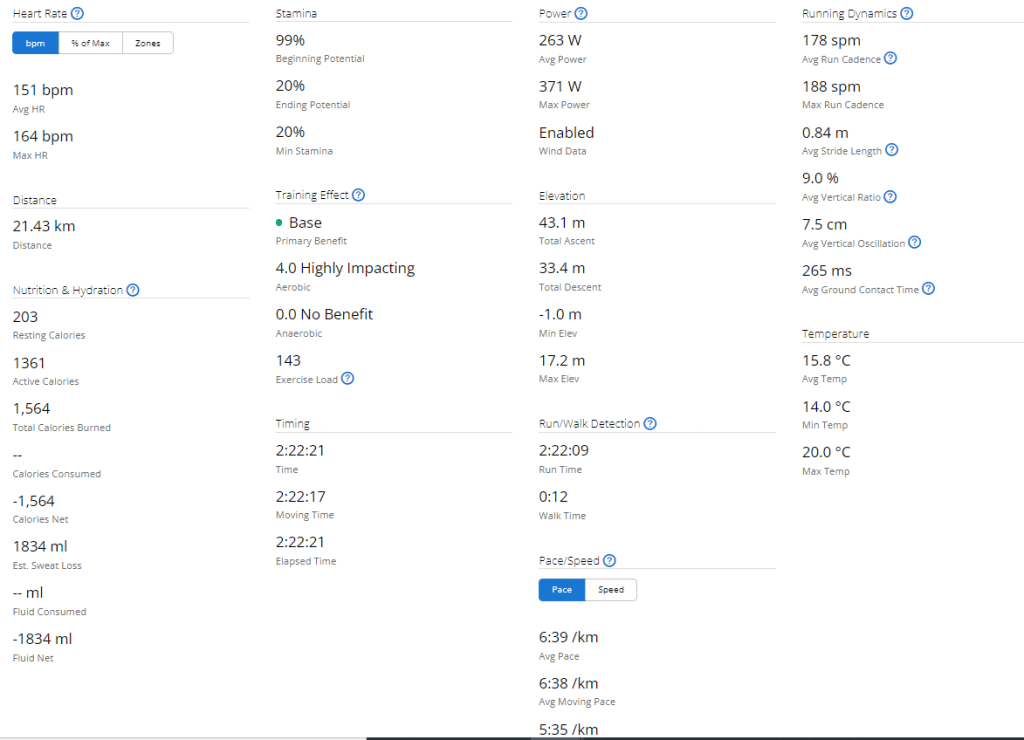
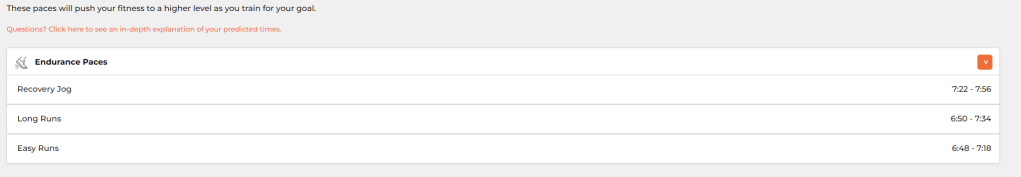
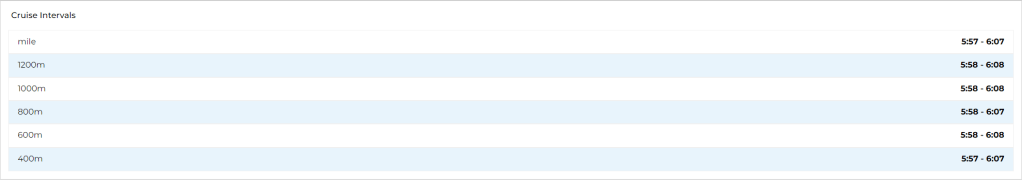
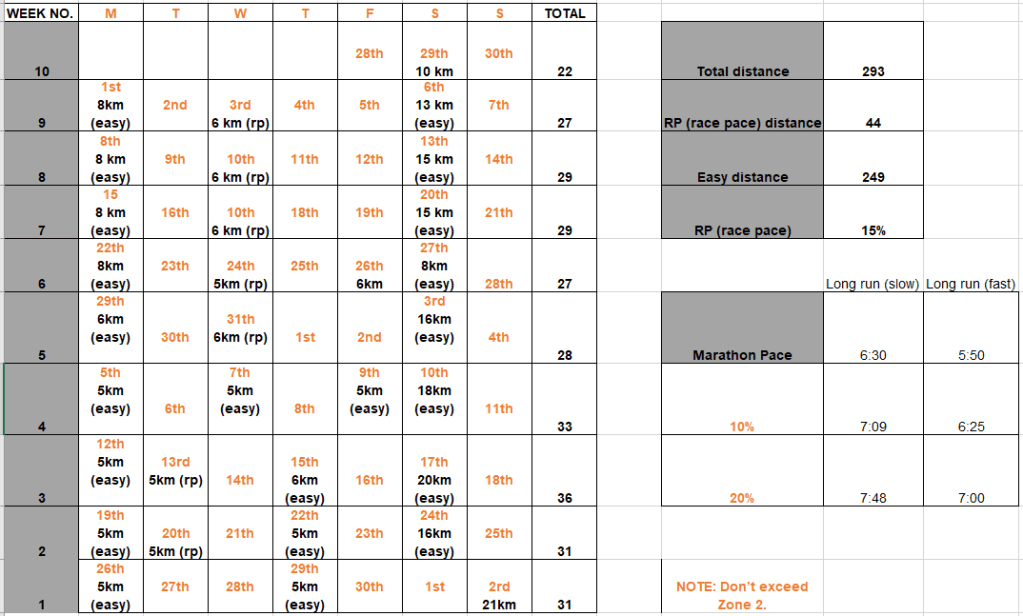
06/06/2023
What is CGM?
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is a technology that allows people with diabetes to track their blood sugar levels in real time. A CGM sensor is inserted under the skin and measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds the cells. The sensor sends readings to a receiver or smartphone every few minutes, so you can see how your blood sugar levels are changing throughout the day.
What is traditional blood glucose testing?
Traditional blood glucose testing involves pricking your finger to draw a drop of blood, which is then applied to a test strip. The test strip is inserted into a blood glucose meter, which provides a reading of your blood sugar level. Traditional blood glucose testing is typically done several times a day, but it can be more frequent if you have diabetes that is not well controlled.
Advantages of CGM
CGM has several advantages over traditional blood glucose testing, including:
- Real-time monitoring: CGM allows you to see your blood sugar levels changing throughout the day, which can help you make better decisions about insulin dosing and food choices.
- More data: CGM provides more data about your blood sugar levels than traditional blood glucose testing. This data can be used to identify trends and patterns in your blood sugar levels, which can help you improve your diabetes management and has allowed for advances like Artificial pancreas systems (APS) to be created.
- Less finger pricks: CGM can help you reduce the number of finger pricks you need to do each day. This can be helpful for people who have diabetes and are sensitive to pain.
Disadvantages of CGM
CGM also has some disadvantages, including:
- Cost: CGM devices can be expensive, and the sensors need to be replaced every 7-10 days.
- Accuracy: CGM sensors are not always accurate, and they can be affected by factors such as exercise, illness, and food.
- Inconvenience: CGM sensors can be uncomfortable to wear, and they can be damaged if they are not properly cared for.
When to use CGM
CGM is a good option for people with diabetes who want to improve their diabetes management. It is especially helpful for people who:
- Have frequent highs and lows
- Have difficulty controlling their blood sugar levels with traditional blood glucose testing
- Are at risk for hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia
- Are pregnant
What happens when you are dehydrated or playing sports?
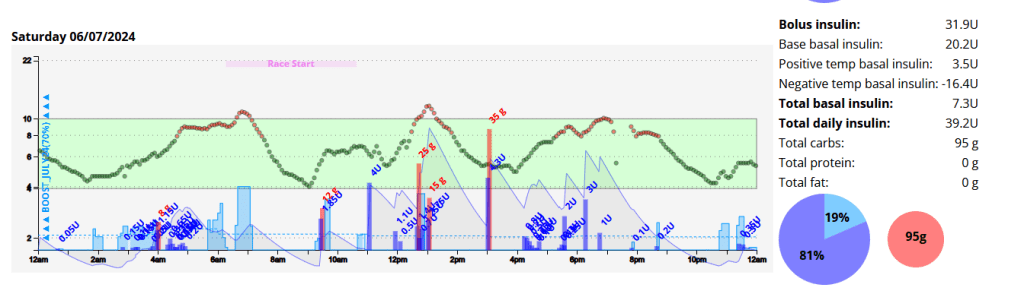
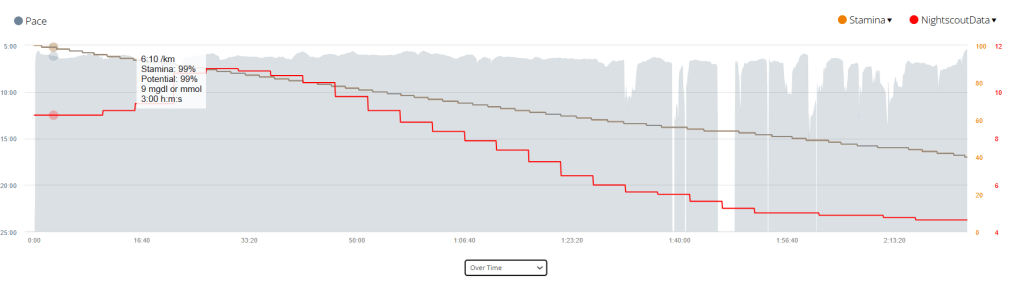
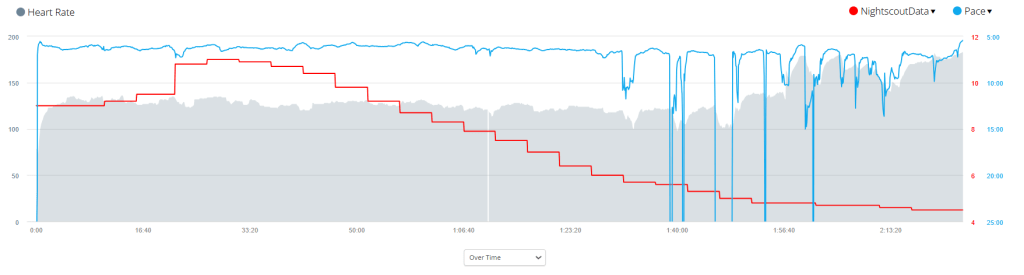
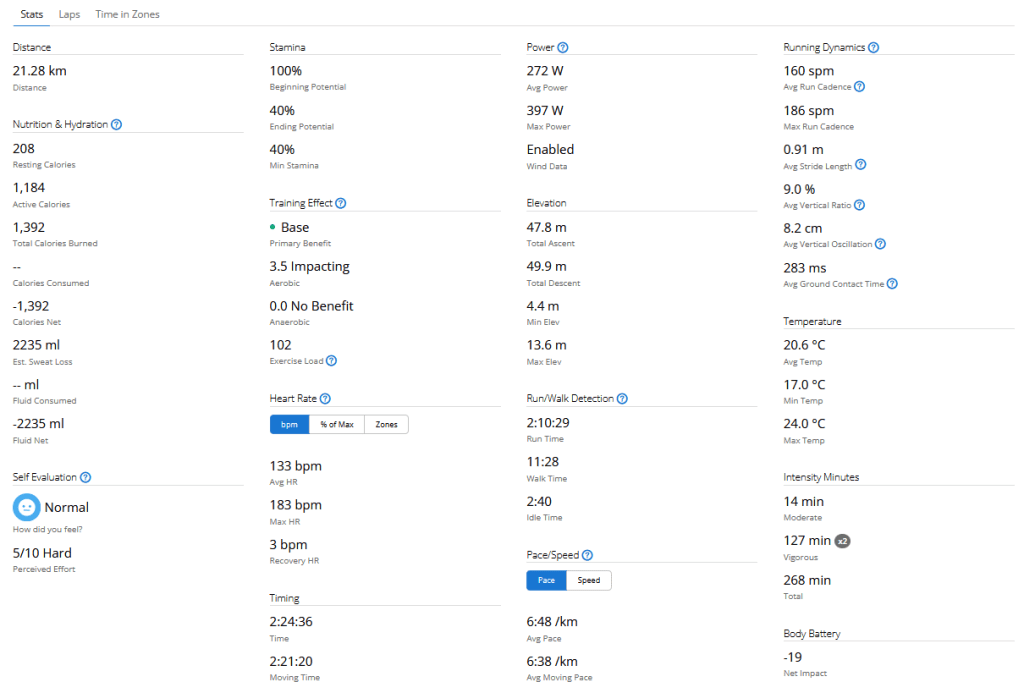
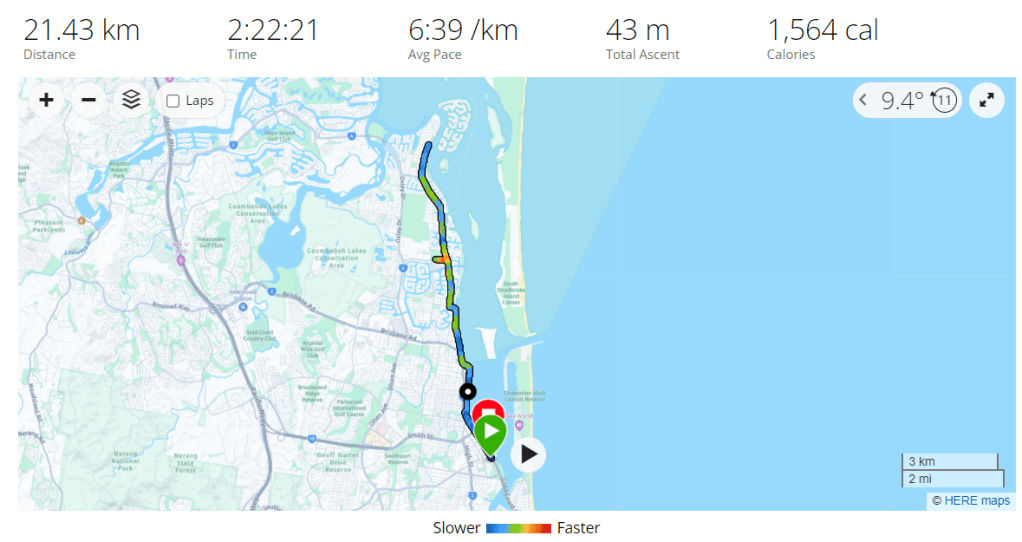
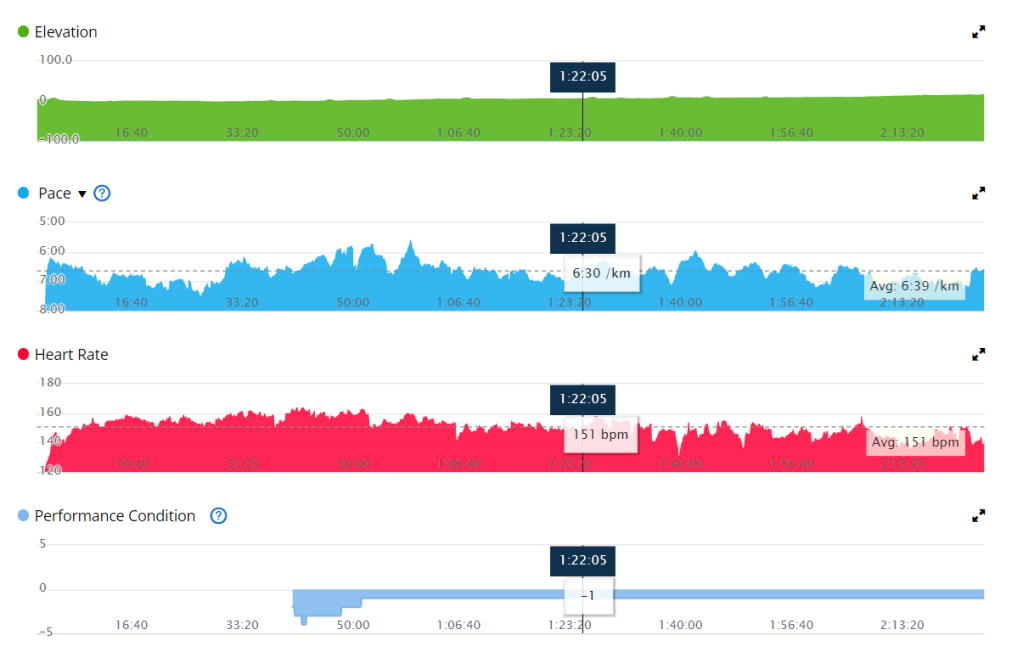
When you are dehydrated, your blood sugar levels can rise. This is because your body is not able to get enough water to flush out excess glucose. When you are playing sports, your blood sugar levels can also rise. This is because your body is using more energy, which can lead to a release of stored glucose.
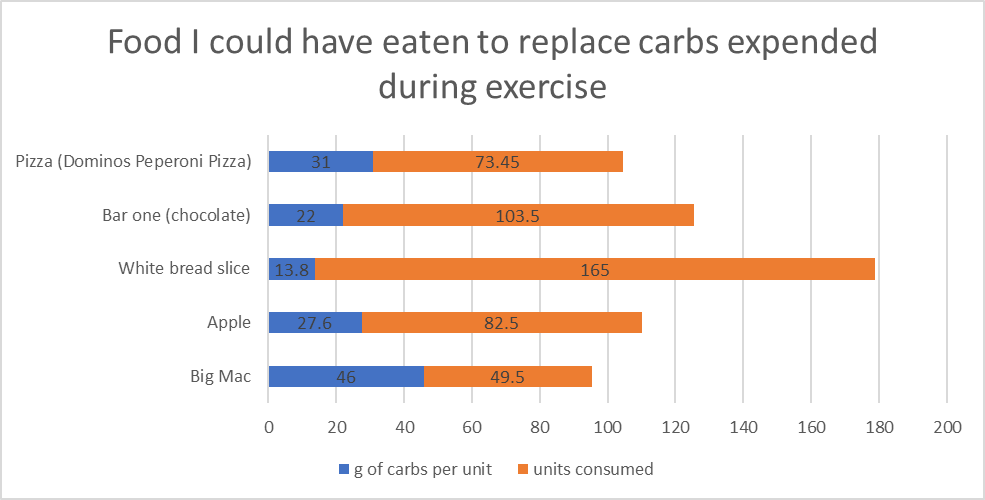
If you are using a CGM, it is important to monitor your blood sugar levels closely when you are dehydrated or playing sports. You may need to adjust your insulin dose or eat more carbohydrates to keep your blood sugar levels in a safe range.
Dexcom sensor settling time
The Dexcom sensor needs about 24 hours to settle after it is inserted. During this time, the sensor may be less accurate. It is important to monitor your blood sugar levels closely during this time and to use a backup method of blood sugar testing, such as a finger prick, if you are concerned about your blood sugar levels.
Sensor placement
The placement of the Dexcom sensor is important. The sensor should be placed on the abdomen or the back of the upper arm. It is important to avoid placing the sensor on areas of the skin that are:
- Injured
- Irritated
- Tattooed
- Scarred
Acceptable tolerance of CGMS and blood sugar testers
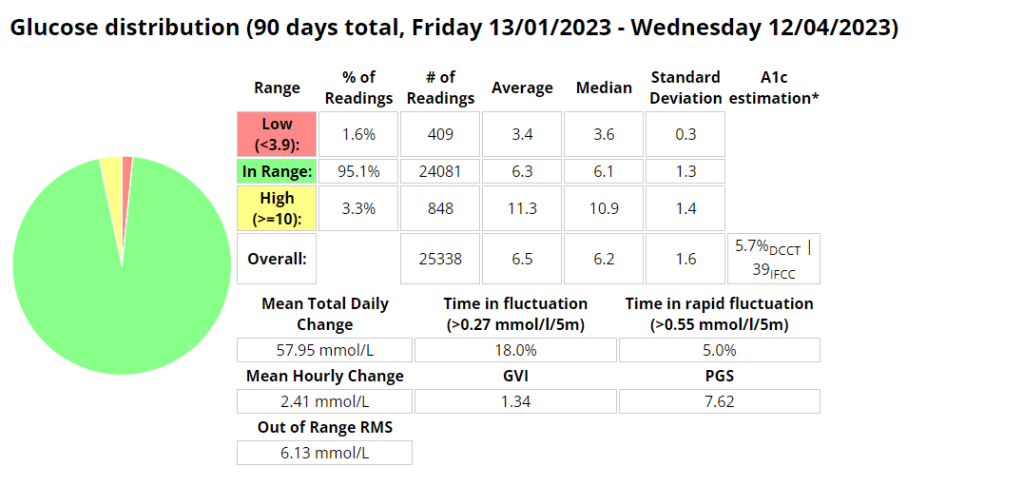
CGMS devices are not always accurate, and they can be affected by factors such as exercise, illness, and food. Dexcom accepts a tolerance of 20% from blood readings. This means that a CGM reading that is 20% higher or lower than a blood reading is still considered to be accurate.
Most finger prick testers can be different to laboratory results. This is because finger prick testers measure blood sugar levels in the blood, while laboratory results measure blood sugar levels in plasma. Plasma is a thicker fluid that contains more glucose than blood. This is why laboratory results are typically higher than finger prick results.
Conclusion
CGM is a valuable tool for people with diabetes. It can help you improve your diabetes management and reduce the risk of complications. If you are considering using a CGM, talk to your doctor about the best option for you.