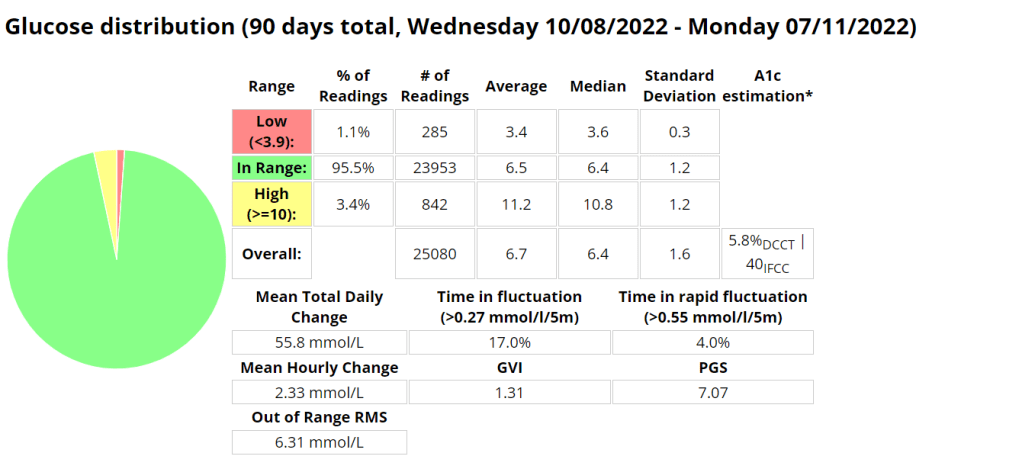
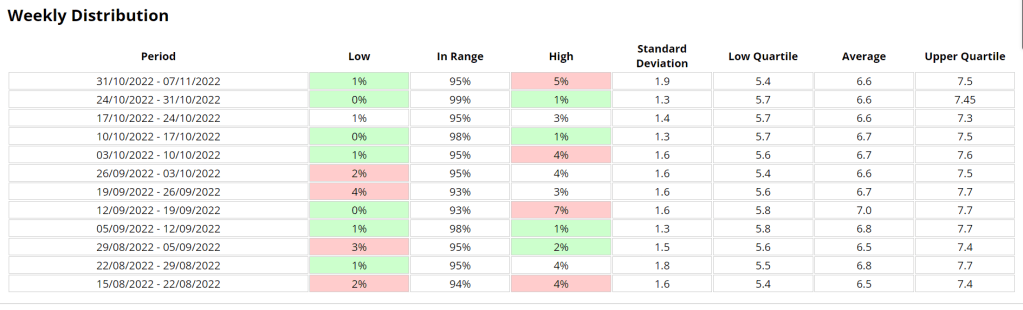
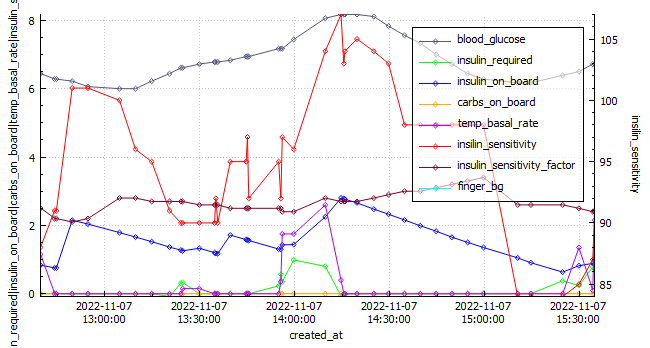
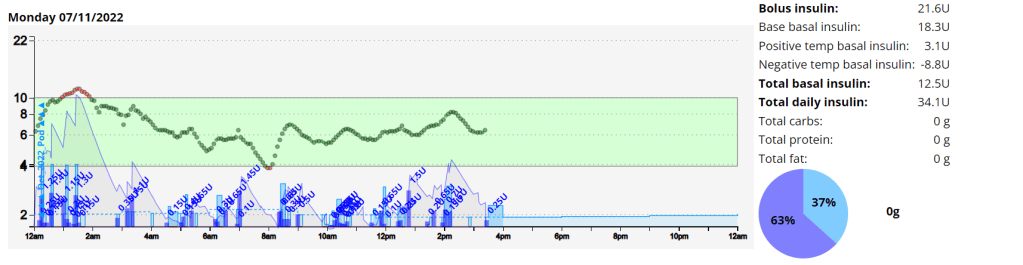
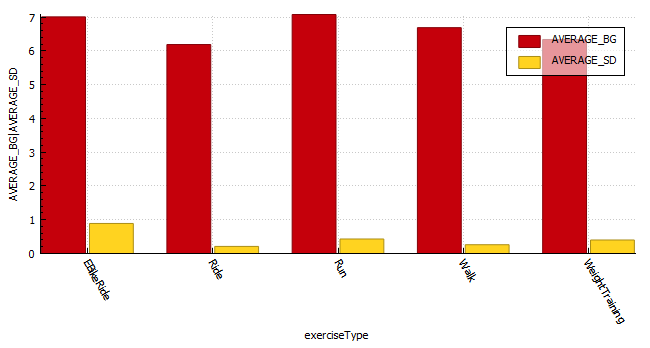
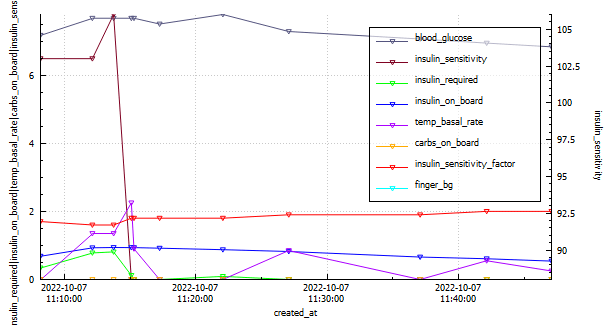
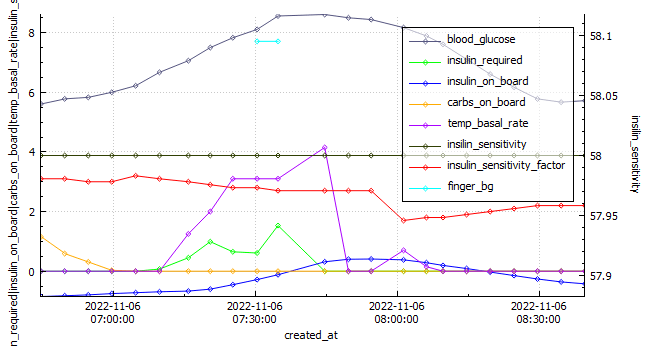
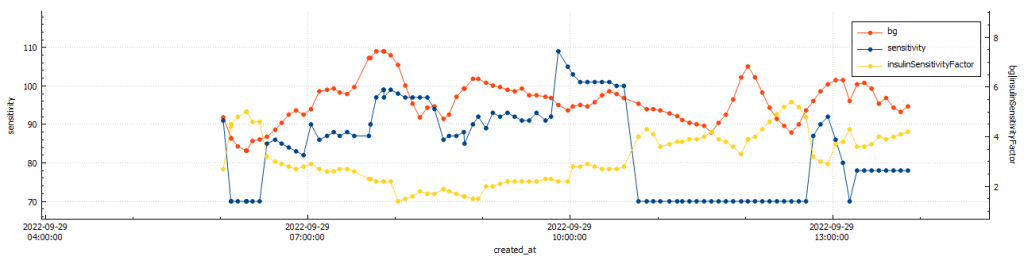
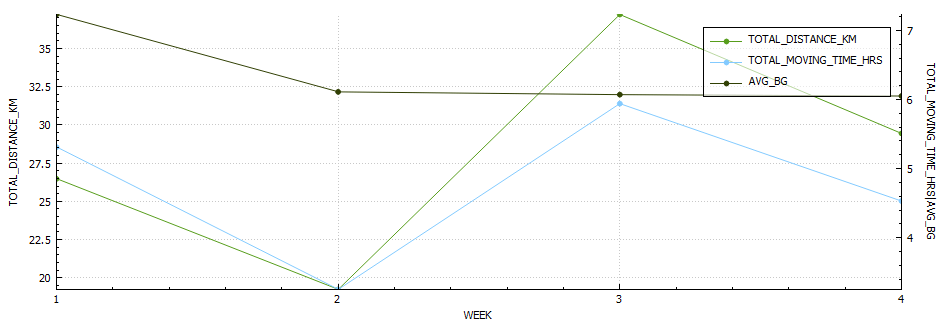
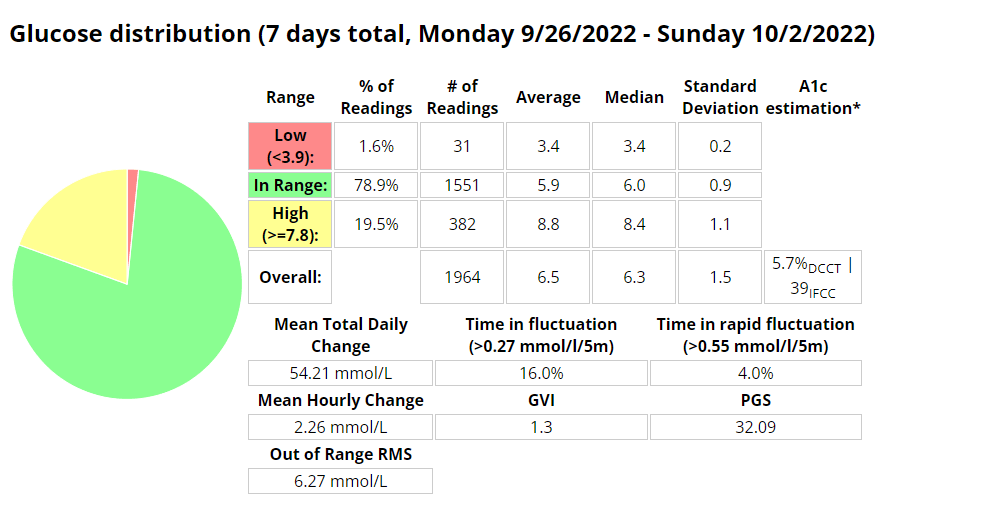
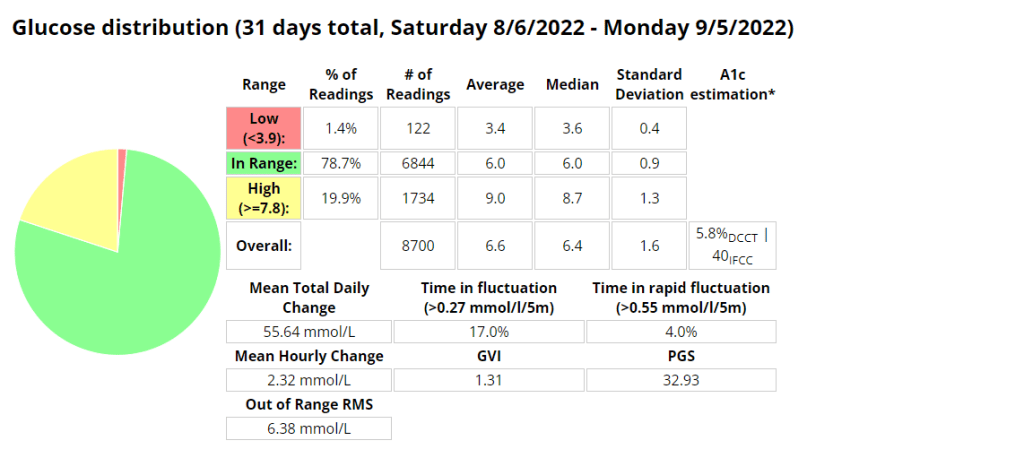
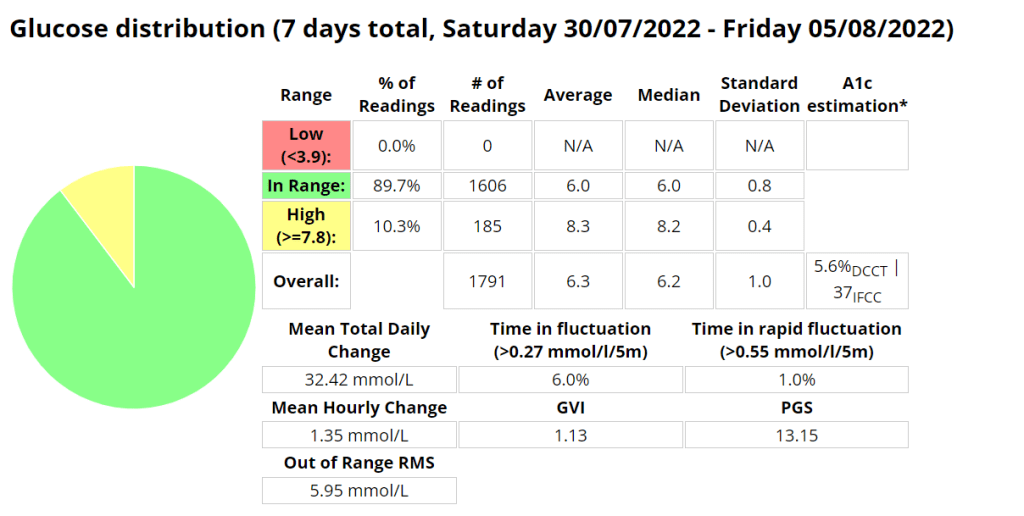
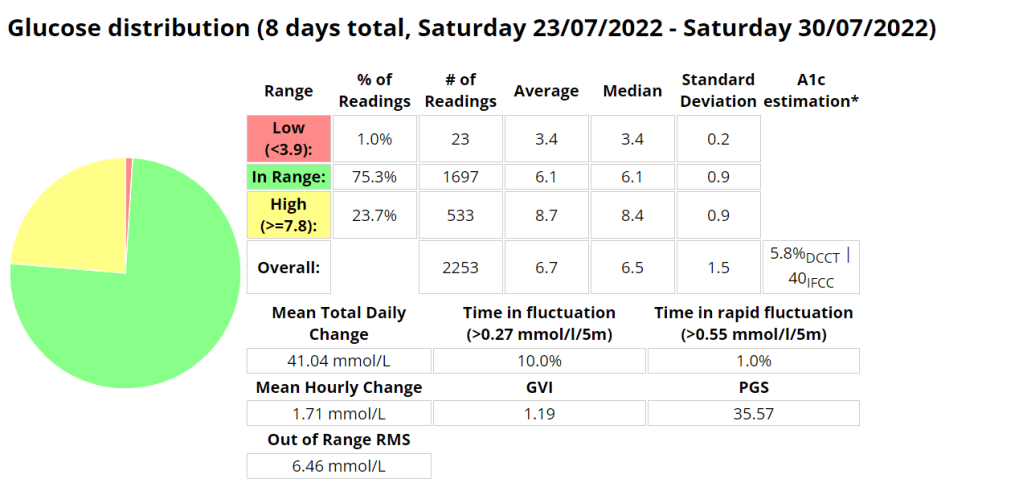
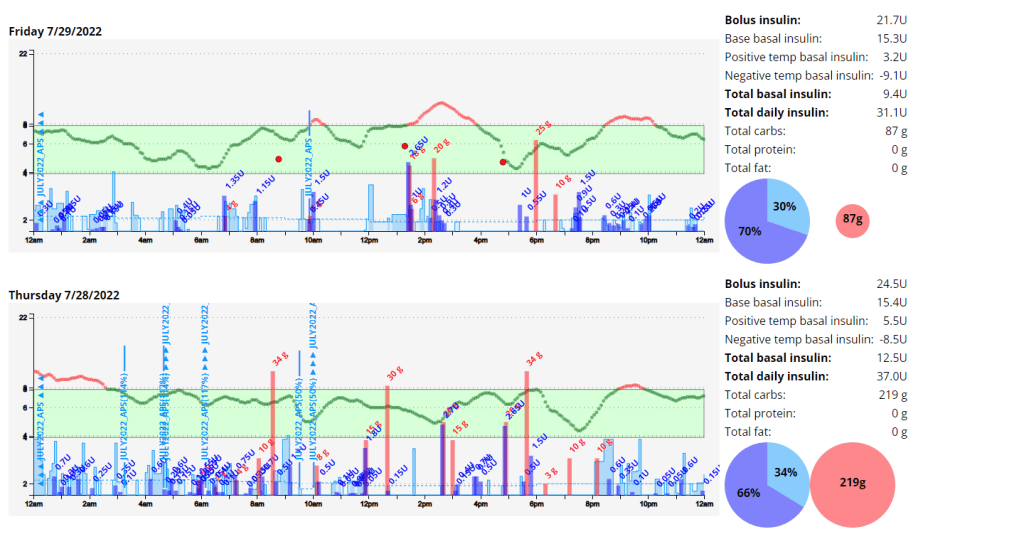
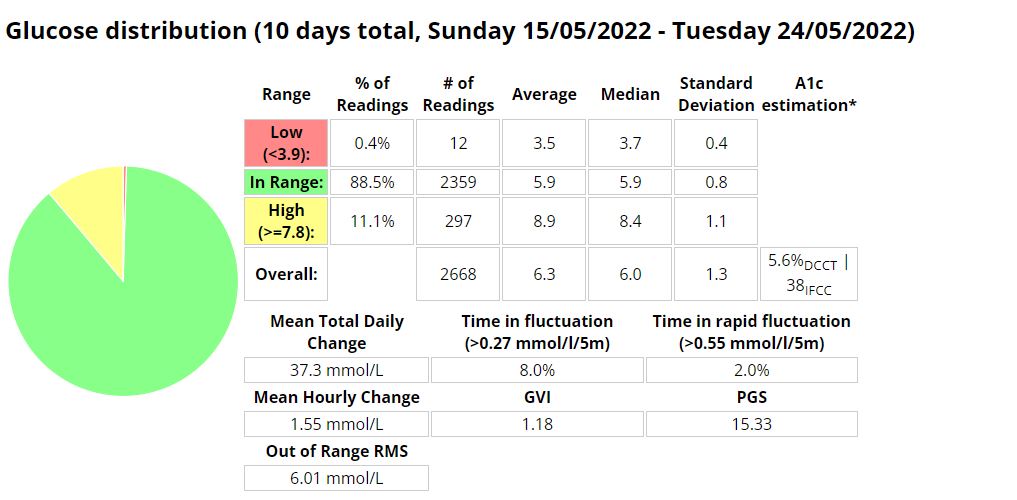
The Glycemic Management Indicator (GMI) is an essential tool used to evaluate and monitor long-term glycemic control in individuals with diabetes. It is derived from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data or frequent fingerstick blood glucose measurements obtained over a specific period, typically ranging from two weeks to three months. GMI is considered an alternative to traditional HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin) measurements, offering a more comprehensive and insightful assessment of glucose management.
- Benefits of GMI Compared to HbA1c:
GMI provides several advantages over traditional HbA1c measurements:
a. Real-Time Data: Unlike HbA1c, which reflects an average of blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, GMI is based on current and recent glucose data. This real-time aspect allows for timely adjustments to diabetes management strategies.
b. More Comprehensive: GMI incorporates a broader range of glucose data, capturing variations and fluctuations in glucose levels that HbA1c may not reveal. It considers both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, offering a more comprehensive view of glycemic control.
c. Better Glucose Trend Assessment: GMI can monitor trends in glucose levels, helping healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes identify patterns and make targeted interventions to improve glycemic management.
- Examples of Using GMI for Glycemic Control Monitoring:a. Personalized Treatment Plans: GMI data enables healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans to individual needs. For instance, if a person has a high GMI with frequent hyperglycemic excursions, treatment adjustments can be made to reduce these excursions and improve overall glycemic control.b. Predicting Hypoglycemia: GMI can help identify periods of increased risk for hypoglycemia, allowing patients to take preventive measures, such as adjusting insulin doses or modifying meal plans.c. Assessing Treatment Changes: When implementing changes in diabetes management, GMI can track the impact of those changes over time, providing valuable feedback on the effectiveness of the modifications.
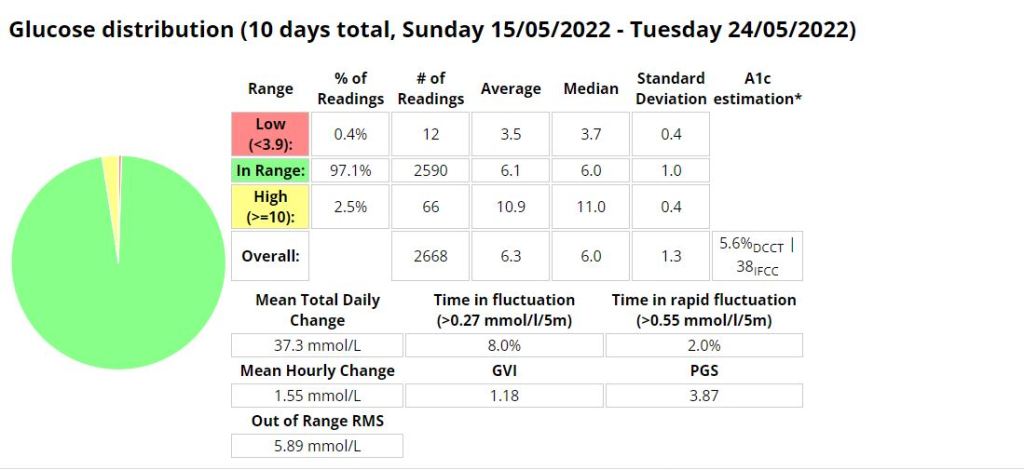
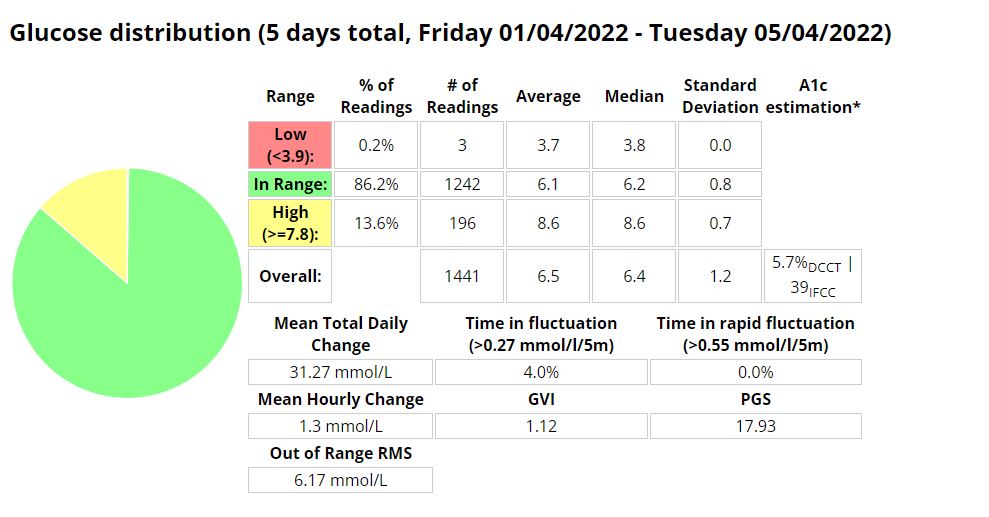
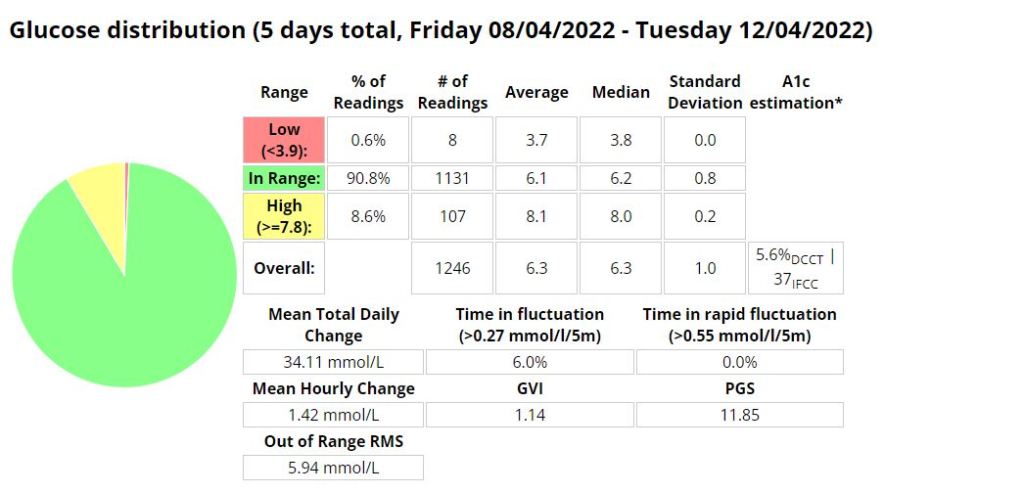
- Addressing Variations in GMI Calculation:The formula to calculate GMI is generally (Mean Glucose + 46.7) / 28.7. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that different devices, CGM systems, and methodologies might use alternative formulas or constants for GMI calculation. To obtain accurate and specific information on GMI calculation, users should refer to the guidelines and documentation provided by the manufacturer of the CGM device or the healthcare professional overseeing diabetes management. This ensures consistency and proper interpretation of GMI results.
In summary, GMI is a valuable tool in diabetes management, offering real-time insights and a more comprehensive assessment of glycemic control compared to traditional HbA1c measurements. By leveraging GMI data, healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes can make informed decisions and take proactive steps to optimize diabetes management strategies.