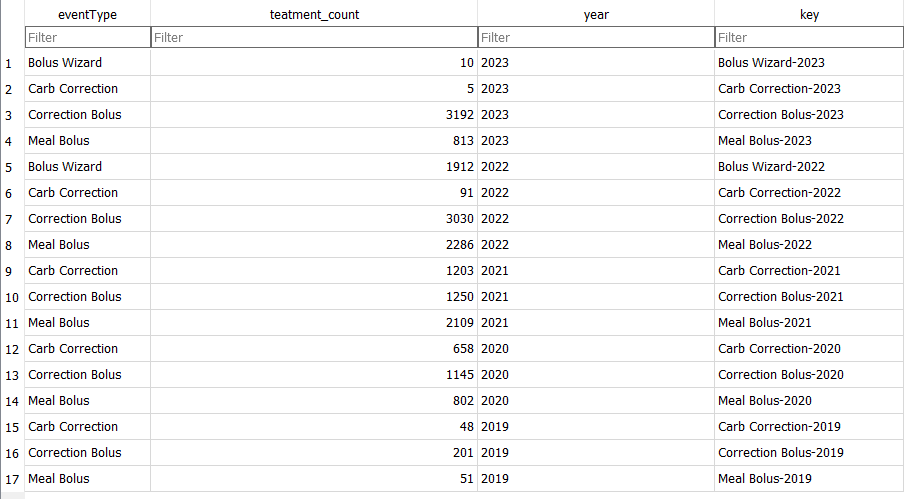14/11/2022
Introduction
It’s diabetes awareness month and so I wanted to talk to you about something I am very passionate about, Android artificial pancreas system (AAPS). It’s not the cure I wanted but as far as I am concerned, it’s the closest to normal I have felt in the 25 years I have been a diabetic.
Why I LOVE Android APS
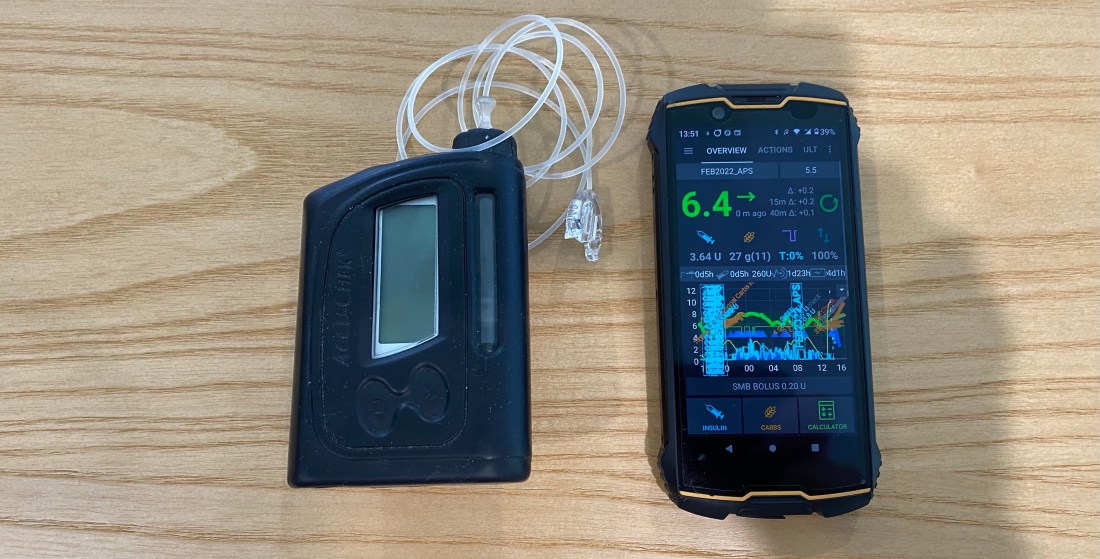
I decided to try Android APS just prior to the birth of my daughter. At the time I was using multiple daily injections (MDI) on a low-carb diet (less than 45g per day excluding protein and fat) and trying to pick up some muscle. I found it rather challenging to eat the number of carbs the trainer suggested without compromising control. I was also anticipating the late nights having a baby entails and I wanted to be prepared. David Burren’s blog provided a blueprint of what could be expected if I committed to investing the time required to perform all necessary testing and fine-tuning.
Benefits of Android APS
- Meal management
- Meals can be managed through a number of mechanisms including;
- Un-announced meals (UAM) – AAPS boluses insulin without intervention or carb entry.
- Announcing carbs – Add the carbs into the system and the calculator estimates the amount of insulin required based on your COB, IOB, ISF, current blood glucose, blood glucose deltas, and insulin sensitivity.
- Extended carbs – typically used to mimic the absorption of protein (gluconeogenesis) or delayed gastric emptying caused by high-fat meals.
- Meals can be managed through a number of mechanisms including;
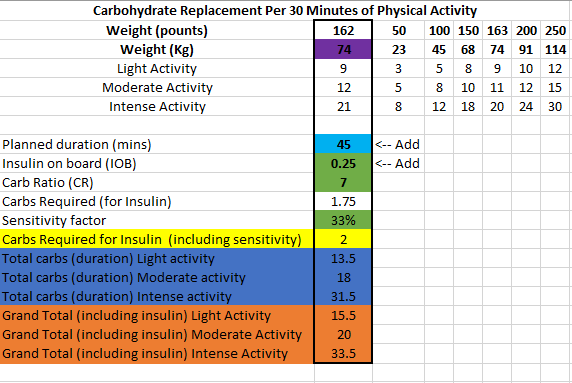
- Exercise management
- Insulin scaling adjusts basal insulin based on current insulin sensitivity
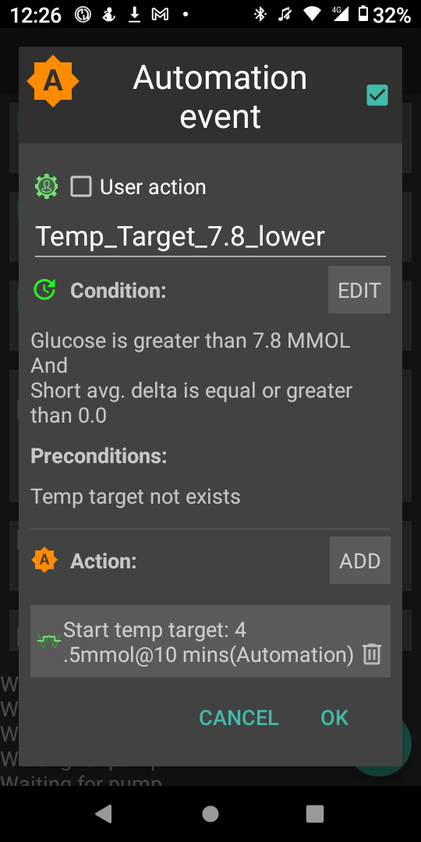
- Automations allow you to schedule profile changes and temporary blood sugar targets for the duration of activity or condition.
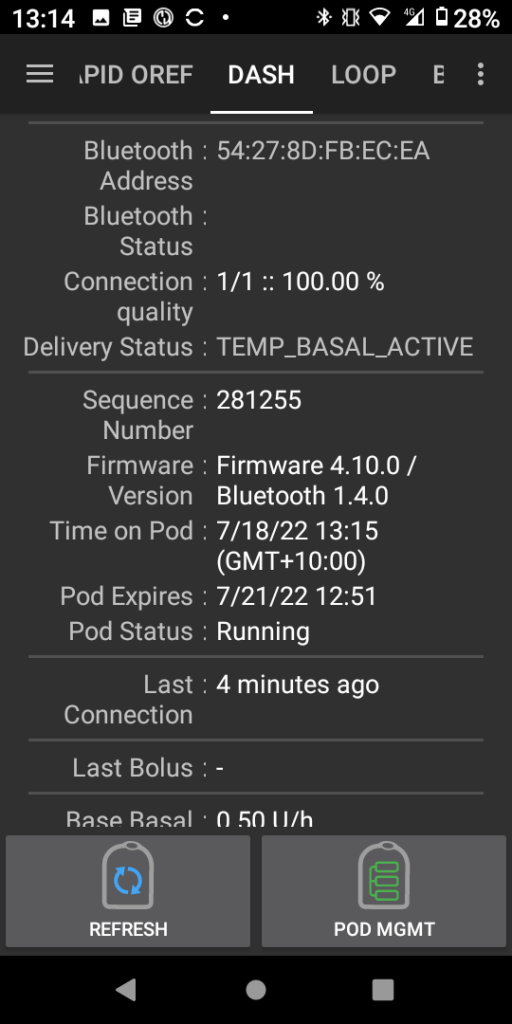
- Hardware / pumps / wearables
- Functional on many old and new low-cost Android phones
- Directly or indirectly (via Nightscout) display various blood glucose-related data on compatible watches. If you are using an Android watch (WearOS) you can control AAPS via the watch. Garmin watches can display blood glucose data during an activity.
- Control a wide variety of pumps
- Utilise the blood glucose data from a wide variety of CGMs (continuous glucose monitors)
- Software
- Automations allow you to automate system actions based on conditions (eg. blood glucose increasing, blood glucose decreasing, leaving for work, pump disconnect) or schedules.
- SMS Commands to control AAPS remotely
- Super micro boluses / boli (SMBs) allow AAPS to provide insulin efficiently and effectively.
- The system will suspend insulin delivery when blood sugar is predicted to go below a certain threshold.
- Can be built on Windows, MacOS and Linux machines.
- Highly customizable to your unique needs, with certain advanced builds allowing you to control more system variables (Boost, AIMI, Eating Now).
- Cutting-edge development
- Dynamic insulin sensitivity factor (ISF that changes based on blood glucose)
- Improved prediction models
- Improved insulin modeling (9-hour DIA)
- Quality of Life
- Reduced diabetic burden and stress.
- Glucose is constantly monitored, with the ability for someone to follow you remotely, including community members. This can assist with fine-tuning settings.
- Ability to eat more foods without compromising control
- Improved glucose control reduces the possibility of long-term complications.
- Safety
- Objectives provide a level of safety as users need to understand basic principles of how to use the APS prior to closing the loop.
- Cost
- AAPS is open-source and free to use.
- Monitoring / Reporting
- A Nightscout site allows you to pull detailed reports, remote monitor (follow) and control AAPS.
- Nightscout reporter provides detailed reports that can assist with APS tuning and a detailed view of your risk rate through the comprehensive glucose pentagon.
- Power BI reporting suite
Dis-benefits of Android APS
- DIY Software build
- As with all DIY systems, you are required to build the application prior to using it.
- Cost of hardware
- Phone
- CGM
- Pump and supplies
- Connectivity fatigue
- The burden of being connected to technology 24/7
- Reliance
- It is easy to become reliant on AAPS managing blood sugars.
- Usability
- Due to its complexity, you are required to invest a large amount of time in order to gain the understanding and skills required to configure and utilise it correctly.
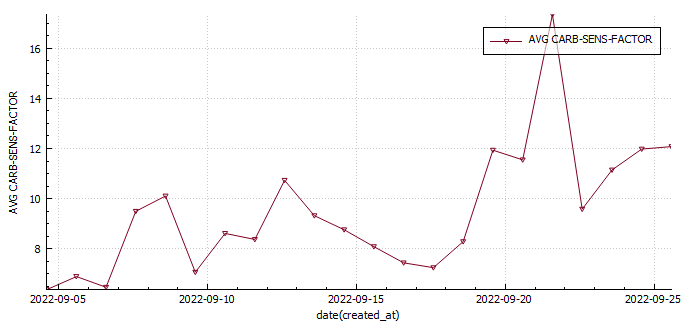
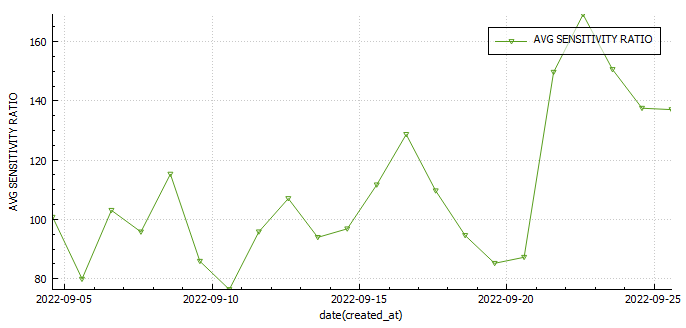
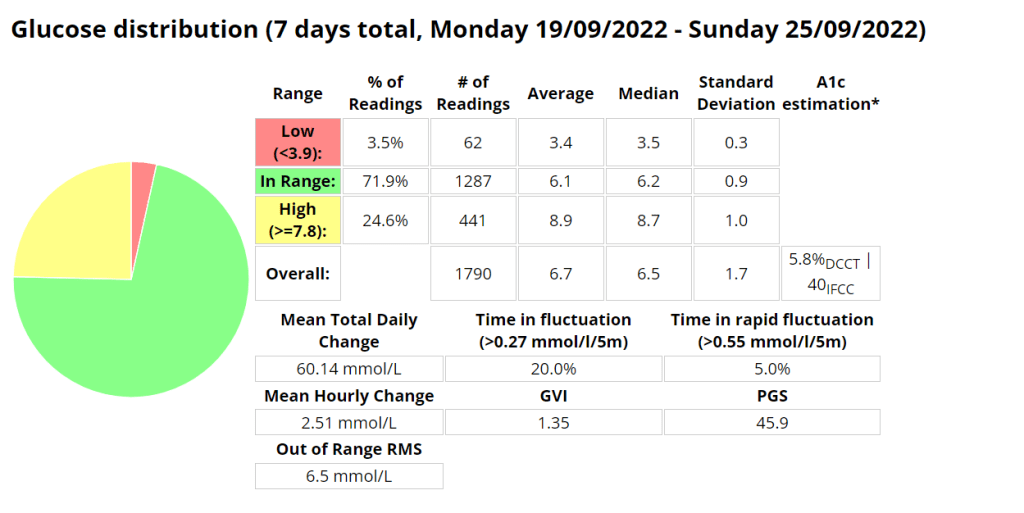
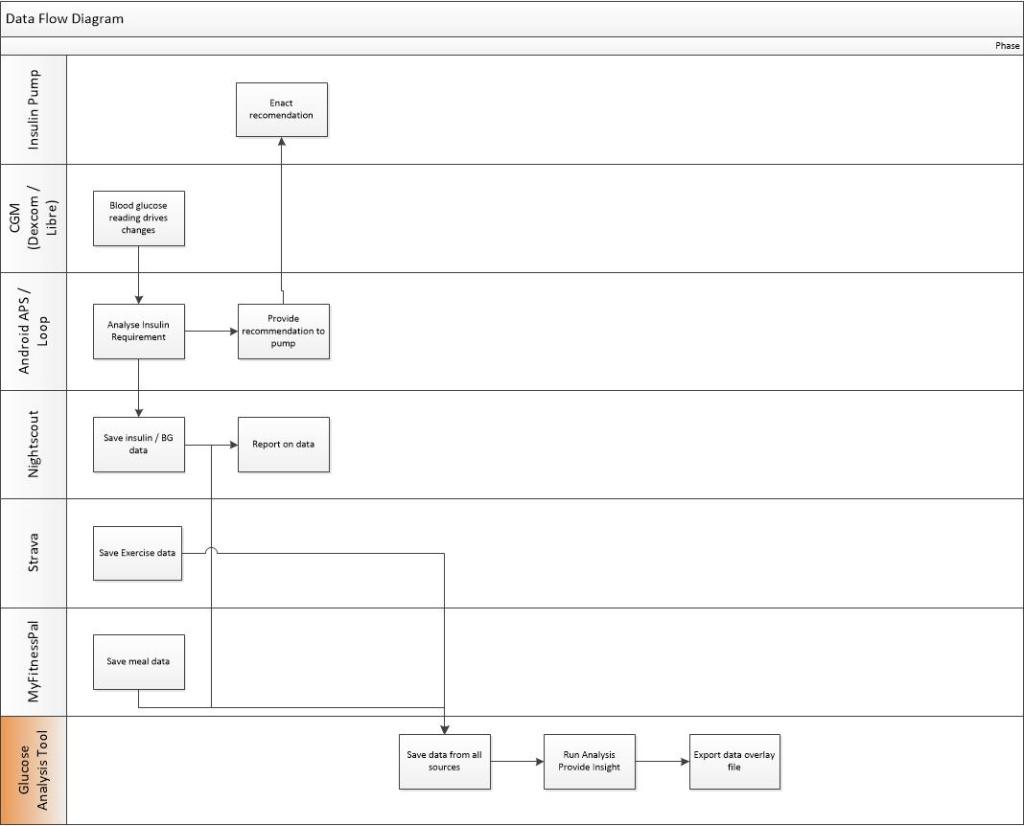
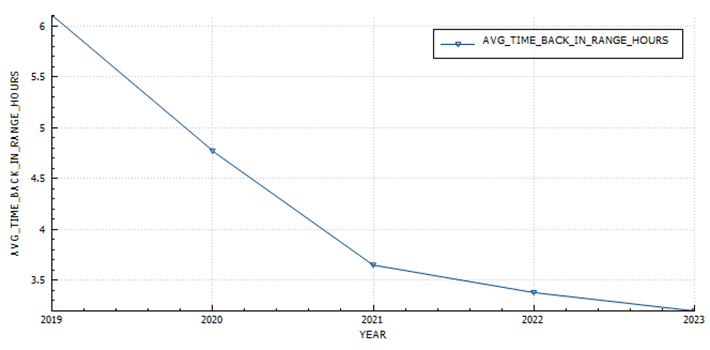
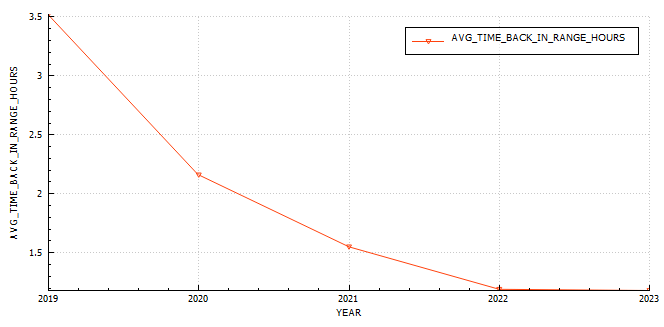
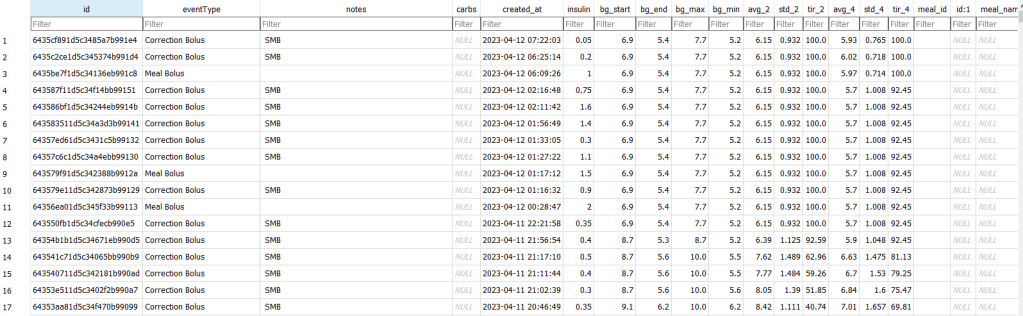
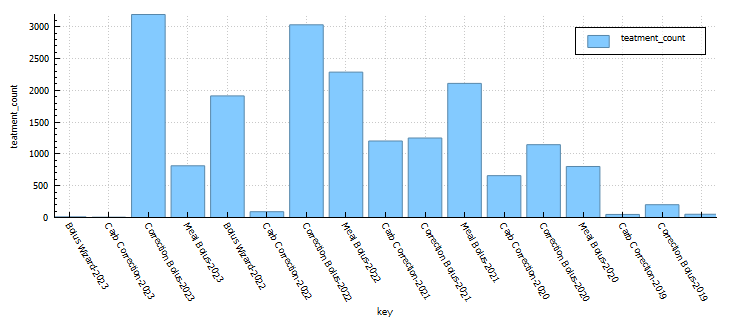
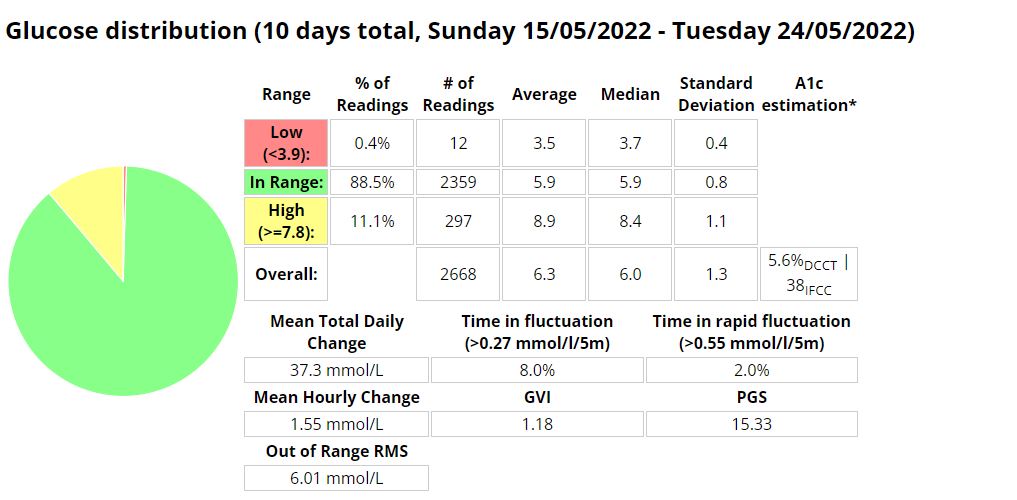
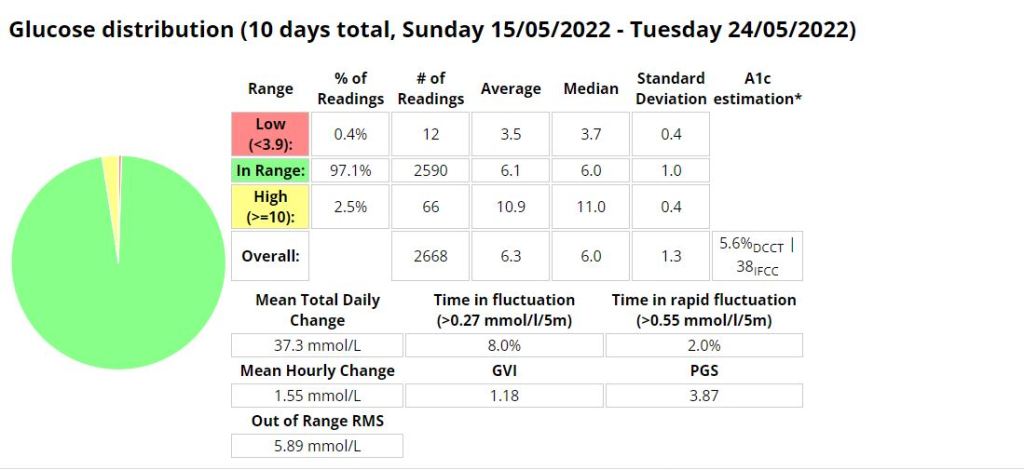
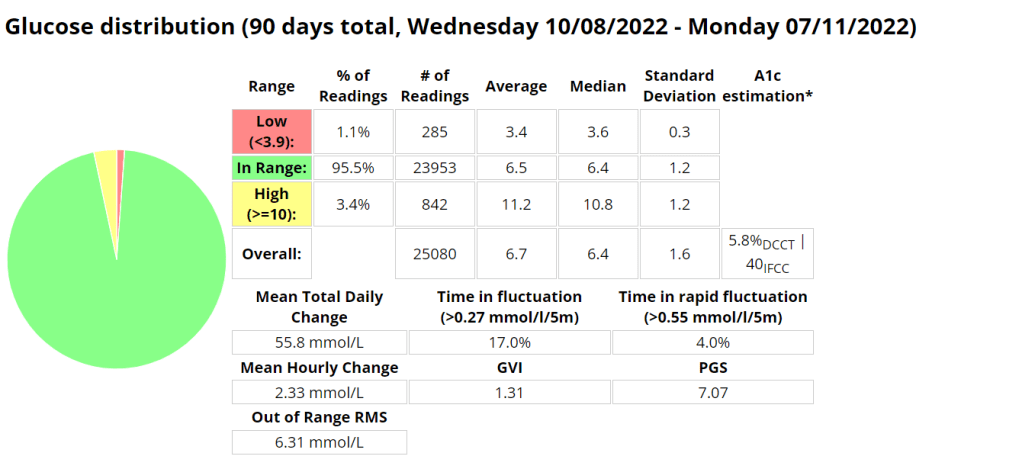
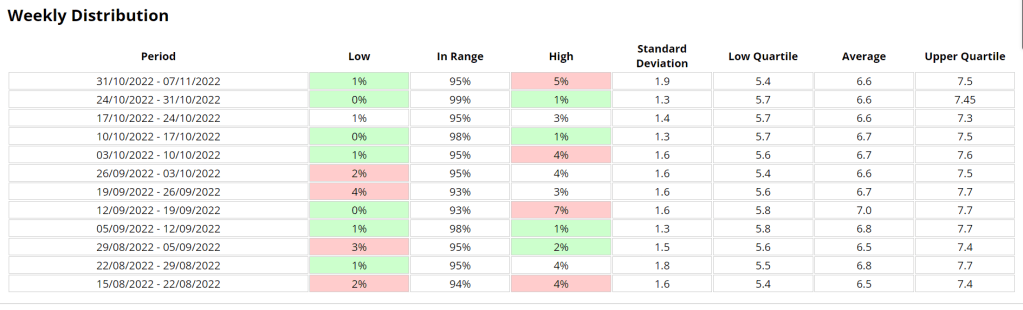
Statistics and examples:
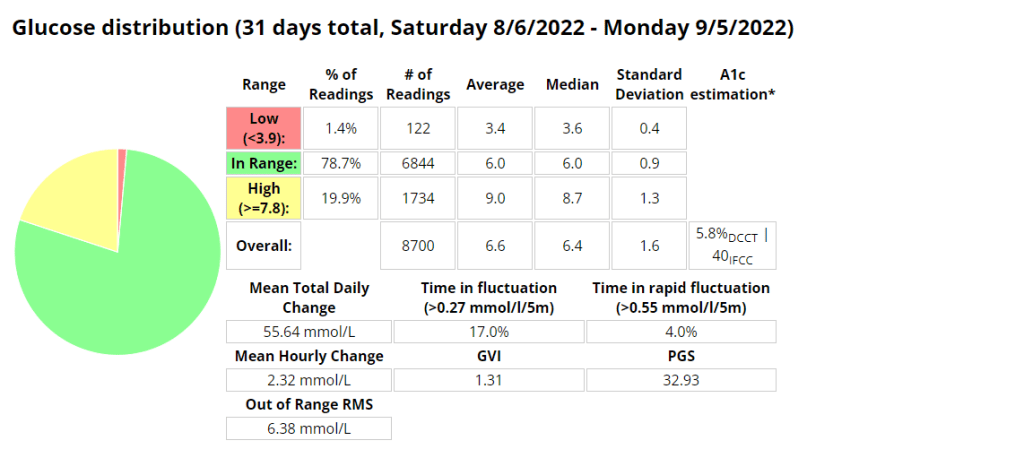
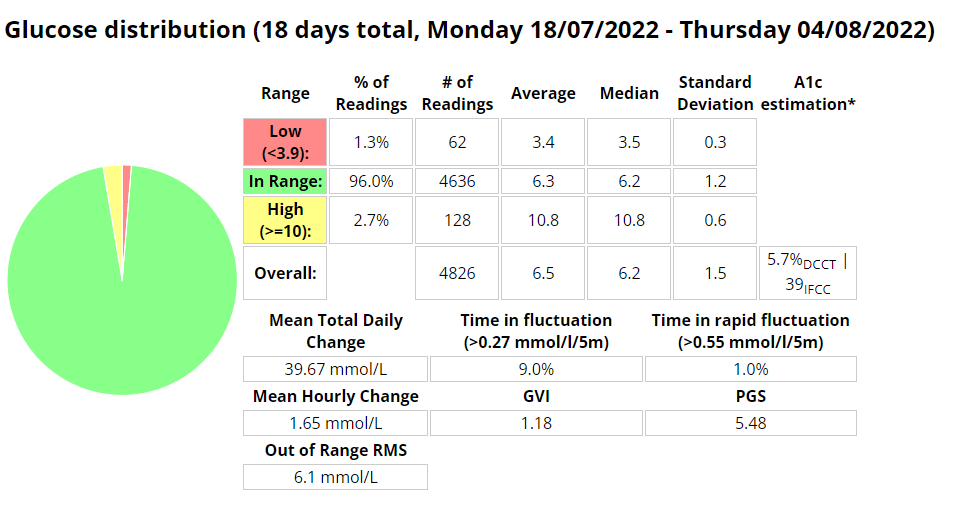
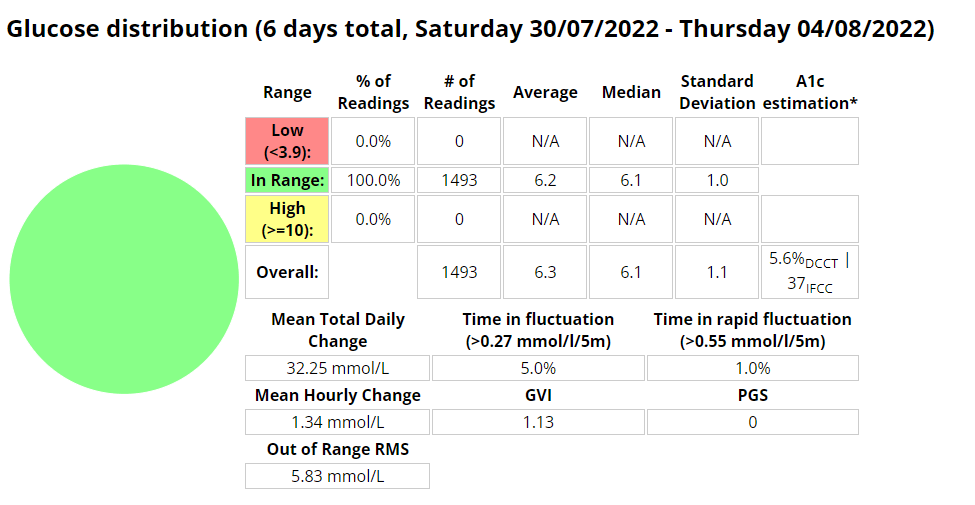
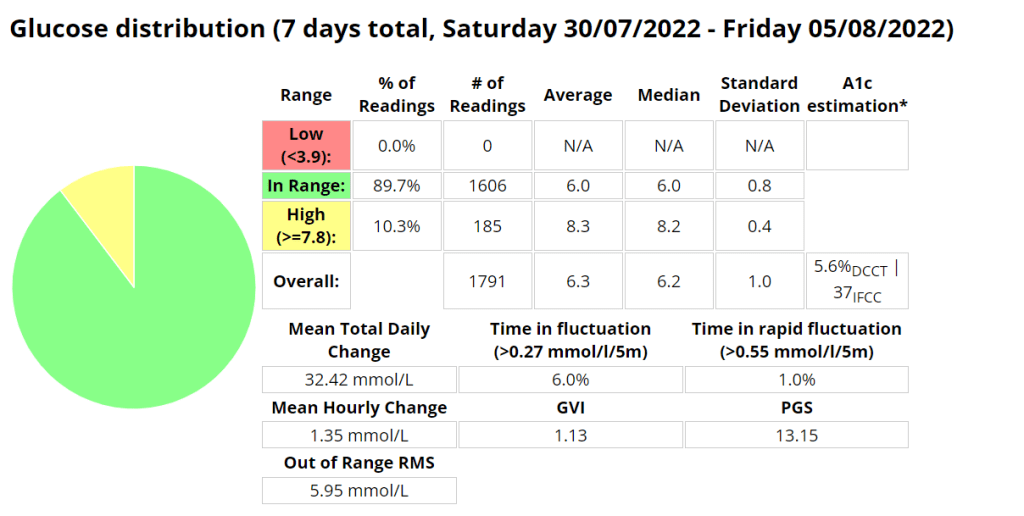
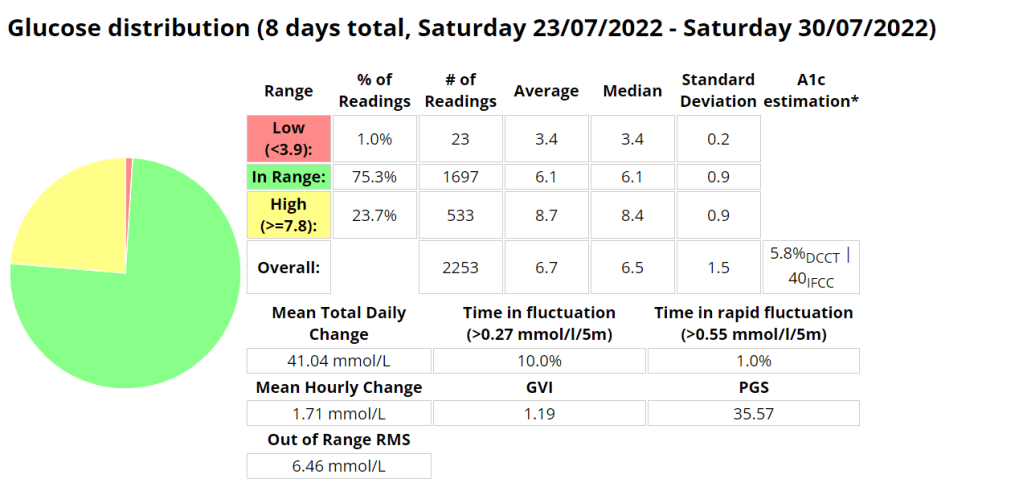
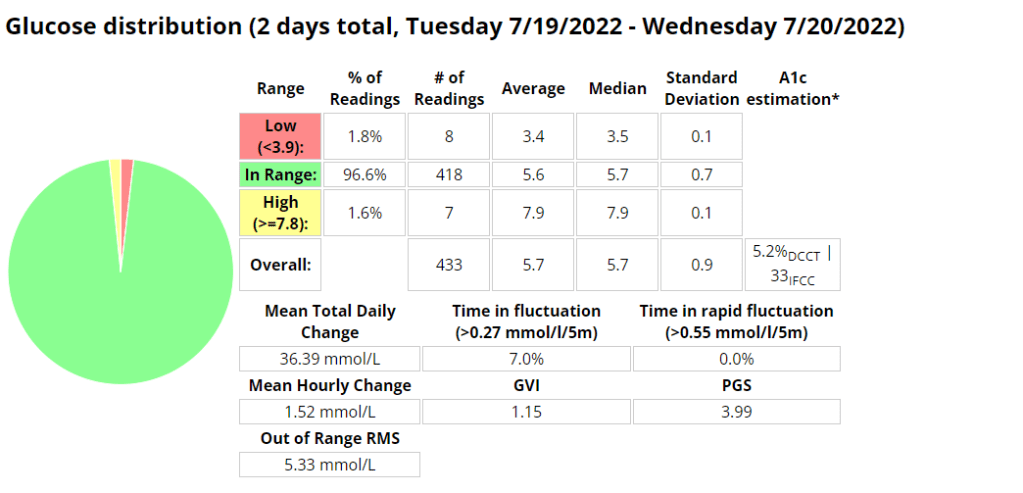
Nightscout statistics – 3 Months
Control stats for different systems
| Date Started Test | Control Mechanism | e-A1C | Average Blood Glucose | Time In Range (TIR) 3.9 – 10 | Standard Deviation | Average carbs consumed | GVI | PGS | CGP – PGR |
| 20/11/2019 | MDI | 6.1% | 7 mmol/l | 87% | 2.2 mmol/l | 1.2 | 20.33 | 1.7 | |
| 20/11/2020 | MDI | 5.6% | 6.3 mmol/l | 94% | 1.7 mmol/l | < 60 | 1.17 | 8.67 | 1.3 |
| 20/11/2021 | Loop | 5.7% | 6.5 mmol/l | 94% | 1.7 mmol/l | <100 (carb counting) | 1.25 | 8.29 | 1.3 |
| 04/02/2022 | Android APS | 5.7% | 6.5 mmol/l | 96% | 1.5 mmol/l | >200, little to no carb counting | 1.24 | 5.70 | 1.2 |

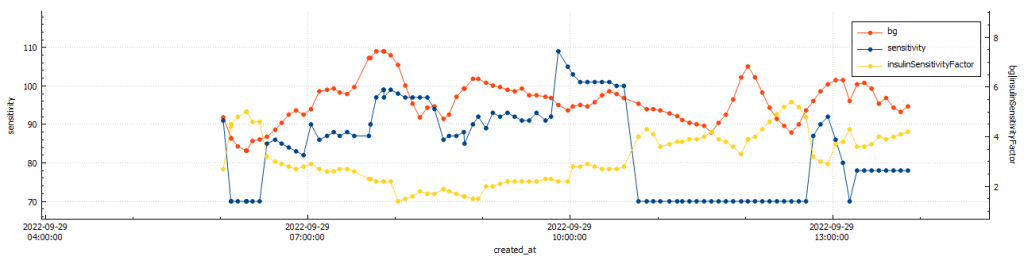
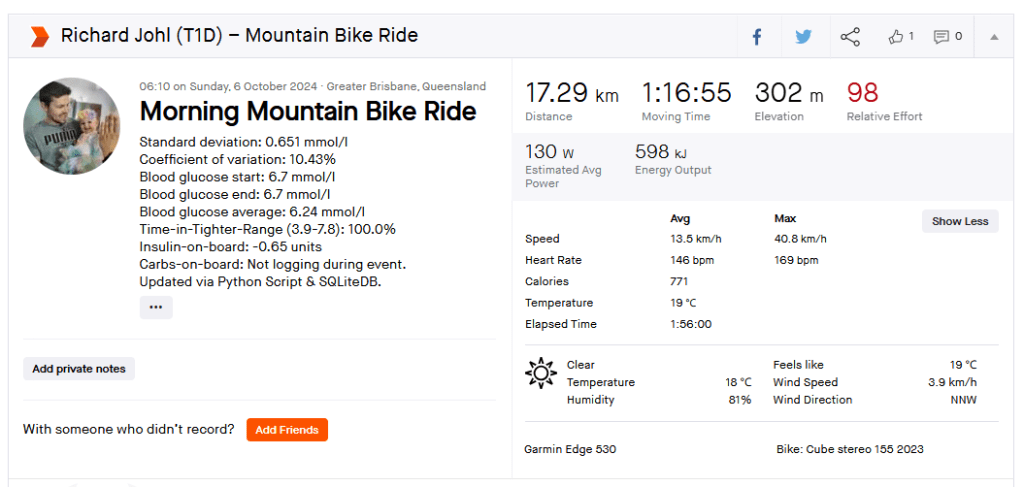
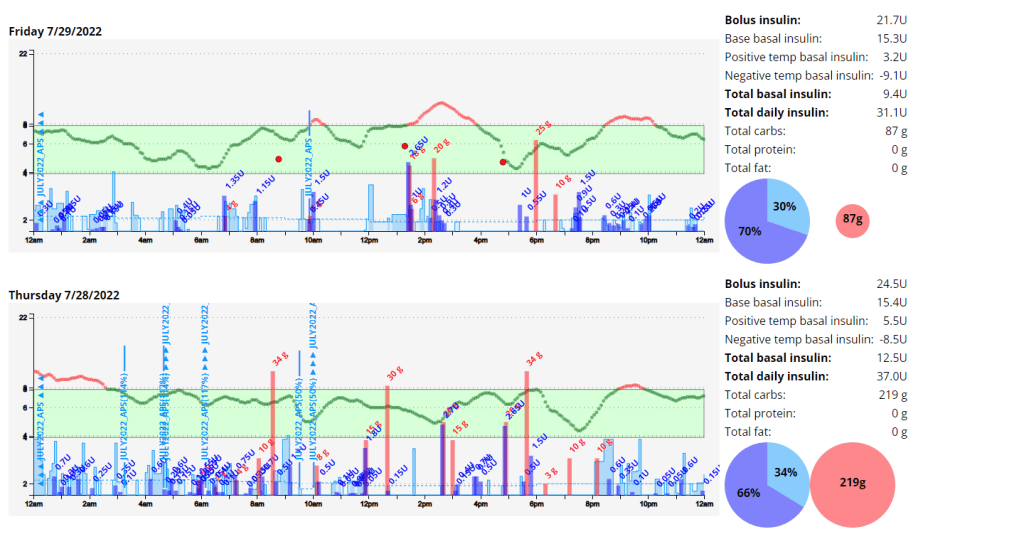
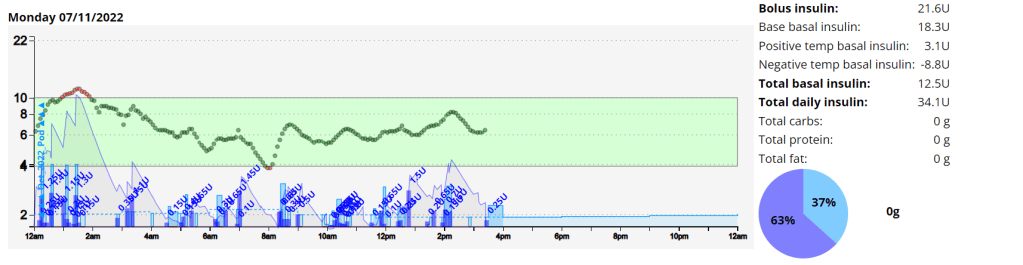
Un-announced meal (UAM) example
Low-carb meal with UAM running (Low-carb bread with cheese, ham, and mayo.)
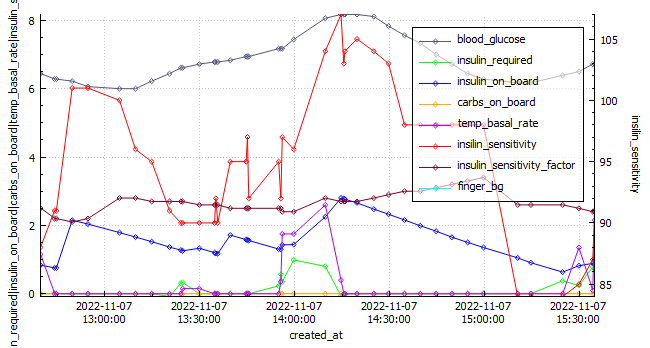
As can be seen above the system manages low-carb meals quite well with no carb inputs from the user. The system constantly monitors for rapid changes in blood sugars and administers insulin when required to quickly brings sugars into range.
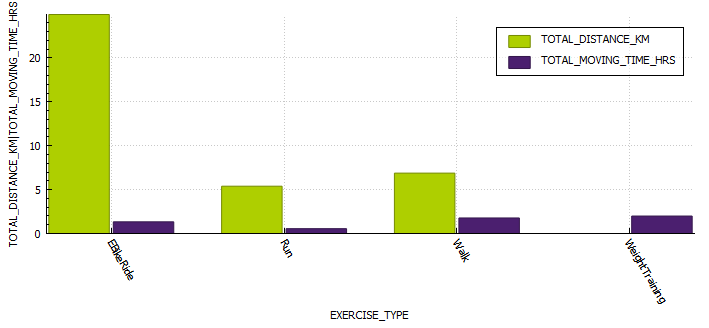
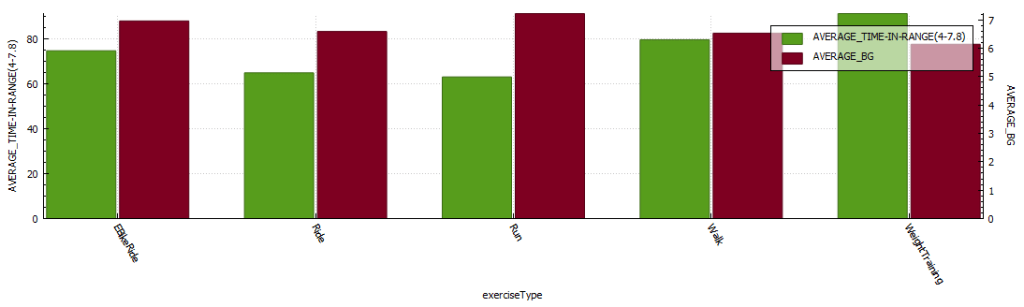
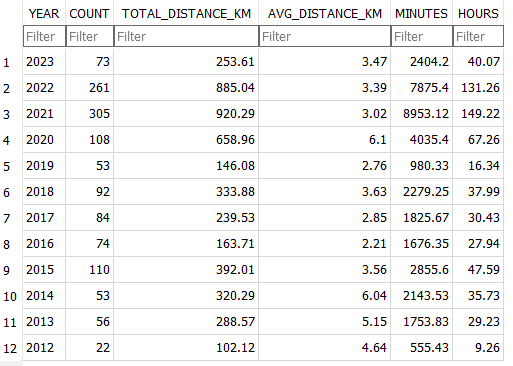
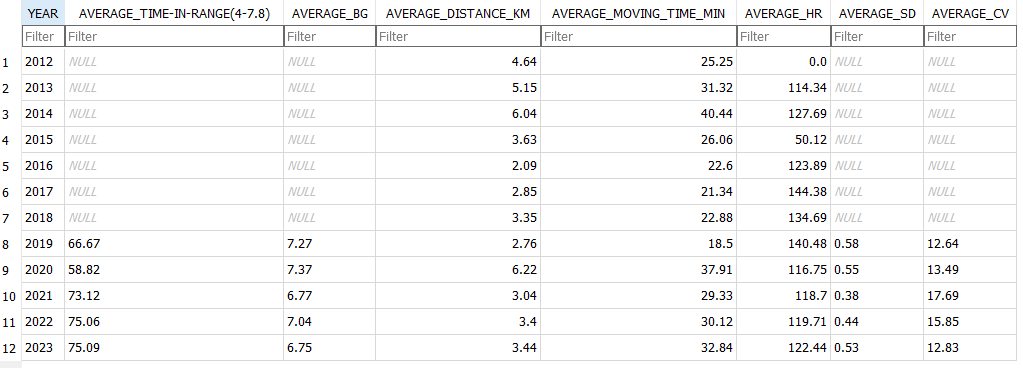
Exercise stats / examples
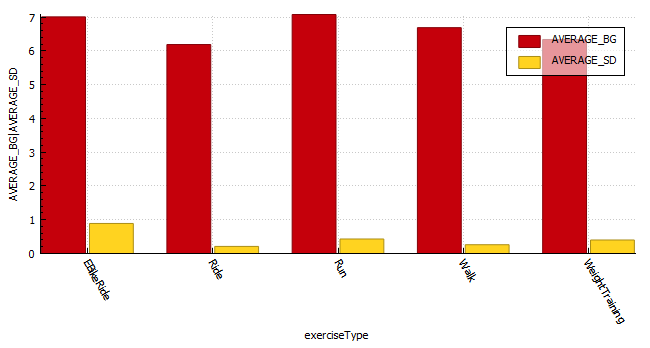
| Year | Average Time in Range (3.9-7.8 mmol/l) | Average blood glucose (mmol/l) | Average Standard Deviation (mmol/l) | Total Hours | Total KM |
| 2022 | 80.1 % | 6.6 | 0.43 | 131 | 885 |
| 2021 | 71.9 % | 6.7 | 0.4 | 149 | 920 |
| 2020 | 69.7 % | 6.9 | 0.7 | 67 | 658 |
Weight Training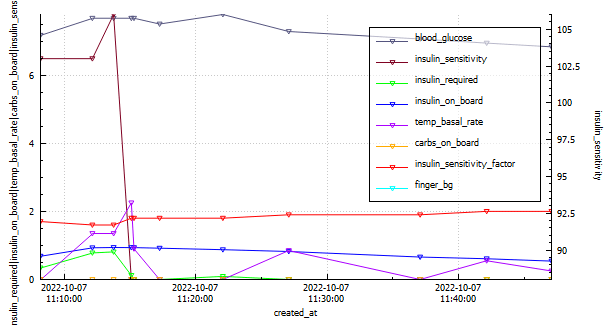
| Date | IOB @ start | Moving time | Exercise Type | Average HR (bpm) | Standard Deviation (mmol/l) | CGM BG Start | CGM BG End | CGM BG Average (mmol/l) | TIR (3.9-10) |
| 2022-10-07 | 0.14 | 36.93 | WeightTraining | 101.1 | 0.365 | 7.7 | 6.8 | 7.27 | 100.0% |
EBike Ride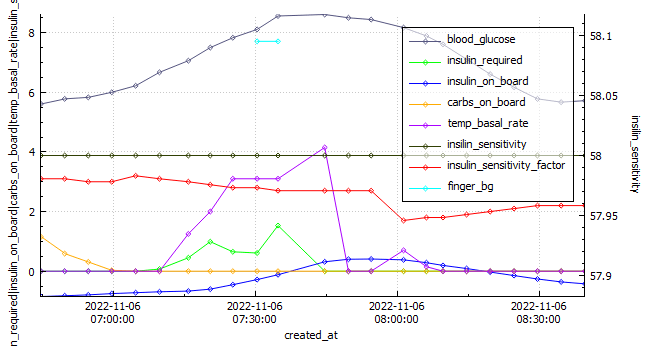
| Date | IOB @ start | Moving time | Exercise Type | Distance (km) | Average HR (bpm) | Standard Deviation (mmol\l) | CGM BG Start | CGM BG End | CGM BG Average (mmol\) | TIR (3.9-10) |
| 2022-11-06 | -0.849 | 115.92 | eBikeRide | 27 | 143 | 1.095 | 5.9 | 5.8 | 7.16 | 100% |
Running
| Date | IOB @ start | Moving time | Exercise Type | Distance (km) | Average HR (bpm) | Standard Deviation (mmol\l) | CGM BG Start | CGM BG End | CGM BG Average (mmol\) | TIR (3.9-10) |
| 2022-10-03 | -0.534 | 78 | Run | 12 | 168 | 1.105 | 5.5 | 5.1 | 6.75 | 100% |